Class 10 AI Unit 2: Advanced Concepts of Modelling in AI – AI vs ML vs DL Notes with Practice Worksheet

Revisiting AI, ML and DL
To build an AI based project, we need to work around Artificially Intelligent models or algorithms. This could be done either by designing your own model or by using the pre-existing AI models.
Definition of AI, ML and DL
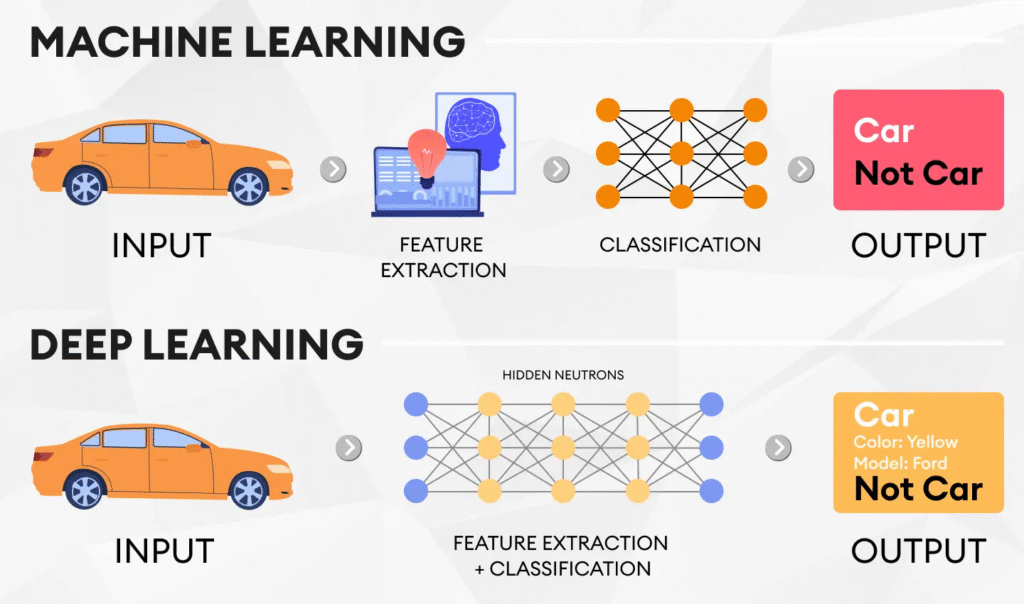
Artificial Intelligence: Artificial Intelligence, or AI for short, refers to any technique that enables computers to mimic human intelligence. An artificially intelligent machine works on algorithms and data fed to it and gives the desired output.
Machine Learning : Machine Learning, or ML for short, enables machines to improve at tasks with experience. The machine here learns from the new data fed to it while testing and uses it for the next iteration. It also takes into account the times when it went wrong and considers the exceptions too.
Deep Learning: Deep Learning, or DL for short, enables software to train itself to perform tasks with vast amounts of data. Since the system has a huge set of data, it is able to train itself with the help of multiple machine learning algorithms working altogether to perform a specific task.
Differences between AI, ML and DL
Artificial Intelligence is the umbrella term which holds both Deep Learning as well as Machine Learning.
Deep Learning, on the other hand, is the very specific learning approach which is a subset of Machine Learning as it comprises multiple Machine Learning algorithms.
| Artificial Intelligence (AI) | Machine Learning (ML) | Deep Learning (DL) |
| Broad field of creating machines that can perform tasks requiring human-like intelligence (e.g. reasoning, problem-solving). | Subset of AI that enables machines to learn patterns from data and improve performance without being explicitly programmed. | DL is a subset of ML that uses neural networks with multiple layers to learn complex patterns from large amounts of data. |
| Can work with limited data (e.g., rule-based AI). | Requires structured data for training. | Needs vast amounts of data for training complex models. |
| Chatbots, robotics, autonomous systems. | Fraud detection, Recommendation engines. | Image recognition, NLP, autonomous driving systems. |
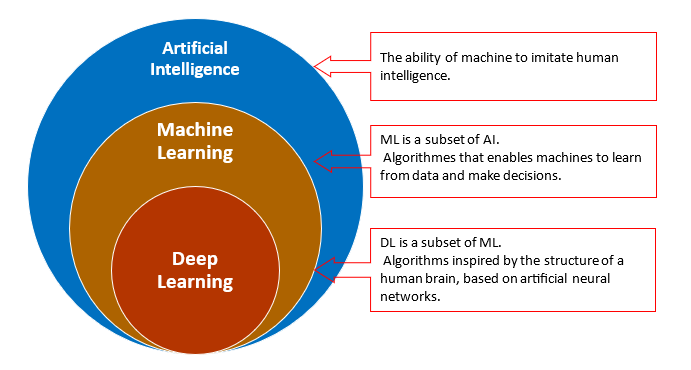
Venn Diagram of AI, ML and DL
As you can see in the Venn Diagram shown in figure,
- Artificial Intelligence is the umbrella terminology which covers machine and deep learning under it and Deep Learning comes under Machine Learning.
- It is a funnel type approach where there are a lot of applications of AI out of which few are those which come under ML out of which very few go into DL.
Artificial Intelligence:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to think and act like humans. This includes capabilities like learning, problem-solving, and decision-making. AI is a broad field encompassing various technologies, including machine learning and deep learning, that enable computers to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence.
Machine Learning
Machine Learning, or ML, enables machines to improve at tasks with experience.
The machine learns from its mistakes and takes them into consideration in the next execution. It improvises itself using its own experiences.
Block Representation – Machine Learning (ML)
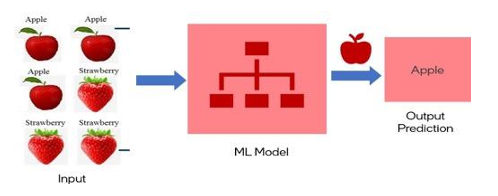
- This is just a broad representation of how a machine learning model works.
- Input (past or historical data) is given to the ML model and the model generates output by learning from the input data.
- Labelled images (every image is tagged either as apple or strawberry) are given as input to the ML model.
- ML model learns from the input data to classify between apples and strawberries and predicts the correct output as shown.

Examples of Machine Learning
- Object Classification
Identifies and labels objects present within an image or data point. It determines the category an object belongs to.
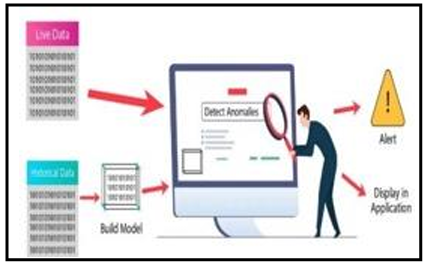
- Anomaly Detection
Anomaly detection helps us find the unexpected things hiding in our data. For example, tracking your heart rate, and finding a sudden spike could be an anomaly, flagging a potential issue.
Deep Learning (DL)
Deep Learning, or DL, enables software to train itself to perform tasks with vast amounts of data.
In deep learning, the machine is trained with huge amounts of data which helps it into training itself around the data. Such machines are intelligent enough to develop algorithms for themselves.
Deep Learning is the most advanced form of Artificial Intelligence out of these three.
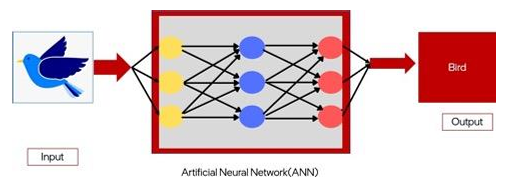
Block Diagram: Following is the block diagram of deep learning:

Input is given to an ANN, and after processing, the output is generated by the DL block.
Here is an example which shows pixels of a bird image given as input to the DL Model and the model is able to analyze and correctly predict that it is a bird using a deep learning algorithm (ANN).
Examples of Deep Learning (DL)
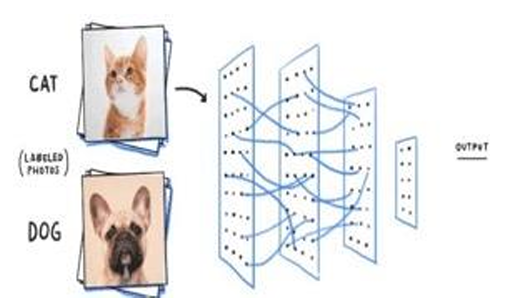
- Object Identification: Object classification in deep learning tackles the task of identifying and labeling objects within an image. It essentially uses powerful algorithms to figure out what’s in a picture and categorize those things.

- Digit Recognition: Digit recognition in deep learning tackles the challenge of training computers to identify handwritten digits (0-9) within images.
Common terminologies used with data
What is Data?
Data is information in any form For e.g. A table with information about fruits is data.
What do you mean by Features?
Each row will contain information about different fruits. Each fruit is described by certain features.
Columns of the tables are called features
What are Labels?
In the fruit dataset example, features may be name, color, size, etc. Some features are special, they are called labels
Data Labeling is the process of attaching meaning to data
- It depends on the context of the problem we are trying to solve
- For e.g. if we are trying to predict what fruit it is based on the color of the fruit, then color is the feature, and fruit name is the label.
- Data can be of two types – Labeled and Unlabeled.
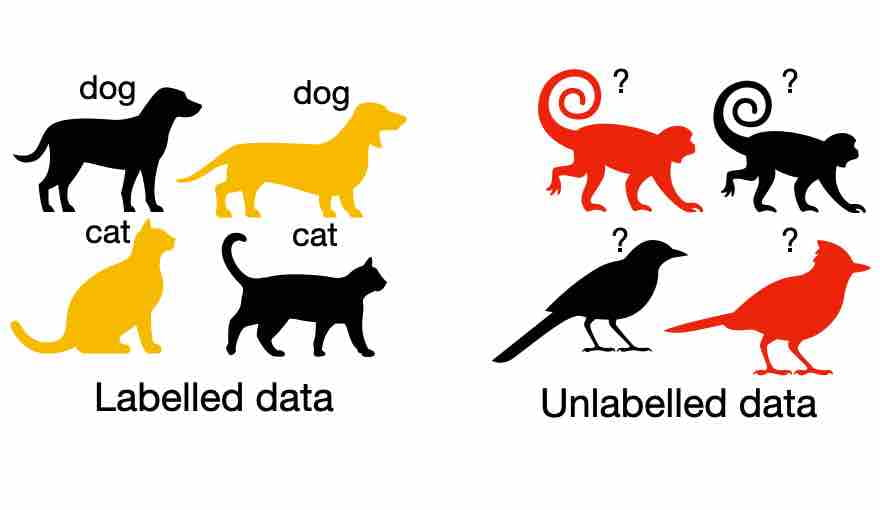
Labeled Data
- Data to which some tag/label is attached. ▪ For e.g. Name, type, number, etc.
Unlabeled Data
- The raw form of data ▪ Data to which no tag is attached.
What do you mean by a training data set?
- The training data set is a collection of examples given to the model to analyze and learn. Just like how a teacher teaches a topic to the class through a lot of examples and illustrations. Similarly, a set of labeled data is used to train the AI model.
What do you mean by a testing data set?
The testing data set is used to test the accuracy of the model. Just like how a teacher takes a class test related to a topic to evaluate the understanding level of students. Test is performed without labeled data and then verified results with labels i.e. testing is done with the help of unlabeled data.
| 2.1 Revisiting AI, ML, DL | Watch Video | Notes, Worksheet & QnA |
| 2.2 (a) AI Modelling – Rule-Based, Learning Based, Machine Learning, Supervised Learning | Watch Video | Notes, Worksheet & QnA |
Worksheet
Class 10 – Artificial Intelligence
Unit 2: Advanced Concepts of Modelling in AI (AI vs ML vs DL)
Section A: Multiple Choice Questions (15)
Q1. Artificial Intelligence primarily refers to:
a) Writing computer programs
b) Simulation of human intelligence in machines
c) Storing large amounts of data
d) Creating websites
Answer: b) Simulation of human intelligence in machines
Q2. Which of the following is an umbrella term?
a) Deep Learning
b) Machine Learning
c) Artificial Intelligence
d) Neural Networks
Answer: c) Artificial Intelligence
Q3. Machine Learning improves performance by:
a) Hard-coded rules
b) User instructions
c) Experience and data
d) Internet speed
Answer: c) Experience and data
Q4. Deep Learning is a subset of:
a) Artificial Intelligence
b) Data Science
c) Machine Learning
d) Robotics
Answer: c) Machine Learning
Q5. Which technique requires the largest amount of data?
a) AI
b) ML
c) DL
d) Rule-based systems
Answer: c) DL
Q6. Which of the following uses Artificial Neural Networks?
a) AI
b) ML
c) DL
d) Rule-based AI
Answer: c) DL
Q7. Identifying apples and strawberries using tagged images is an example of:
a) Anomaly Detection
b) Object Classification
c) Deep Learning
d) Robotics
Answer: b) Object Classification
Q8. Columns in a dataset are called:
a) Rows
b) Records
c) Features
d) Labels
Answer: c) Features
Q9. What is a label in data?
a) Input value
b) Column name
c) Output or target value
d) Dataset size
Answer: c) Output or target value
Q10. Which data has tags attached to it?
a) Raw data
b) Unlabeled data
c) Structured data
d) Labeled data
Answer: d) Labeled data
Q11. The dataset used to teach the model is called:
a) Testing dataset
b) Training dataset
c) Validation dataset
d) Raw dataset
Answer: b) Training dataset
Q12. The testing dataset is mainly used to:
a) Train the model
b) Store data
c) Evaluate model accuracy
d) Remove errors
Answer: c) Evaluate model accuracy
Q13. Detecting a sudden spike in heart rate is an example of:
a) Classification
b) Prediction
c) Anomaly Detection
d) Regression
Answer: c) Anomaly Detection
Q14. Digit recognition (0–9) mainly uses:
a) ML
b) AI
c) DL
d) Robotics
Answer: c) DL
Q15. Which statement is correct?
a) ML is broader than AI
b) DL is a subset of ML
c) AI is a subset of DL
d) DL works with very little data
Answer: b) DL is a subset of ML
Section B: Fill in the Blanks (10)
Q1. Artificial Intelligence enables machines to mimic __________ intelligence.
Answer: human
Q2. Machine Learning improves performance using __________.
Answer: experience
Q3. Deep Learning uses multiple layers of __________ networks.
Answer: neural
Q4. AI models work on __________ and data.
Answer: algorithms
Q5. __________ data has no tags attached to it.
Answer: Unlabeled
Q6. Features are the __________ of a dataset.
Answer: columns
Q7. Fruit name is a __________ when predicting fruit type.
Answer: label
Q8. The testing dataset checks the __________ of a model.
Answer: accuracy
Q9. Deep Learning requires __________ amounts of data.
Answer: vast
Q10. AI, ML and DL follow a __________ type approach.
Answer: funnel
Section C: Short Answer Questions
(Answer in about 30 words)
Q1. Define Artificial Intelligence.
Answer: Artificial Intelligence refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to think, learn, solve problems and make decisions using algorithms and data.
Q2. What is Machine Learning?
Answer: Machine Learning enables machines to learn from data and experience, improve performance over time and make predictions without being explicitly programmed.
Q3. Explain Deep Learning.
Answer: Deep Learning is a subset of Machine Learning that uses multi-layered neural networks to process large amounts of data and perform complex tasks automatically.
Q4. Differentiate between features and labels.
Answer: Features are input variables used for prediction, while labels are the output or target values that the model tries to predict.
Q5. What is labeled data?
Answer: Labeled data is data that has predefined tags or output values attached to it, which helps in training supervised machine learning models.
Q6. What is unlabeled data?
Answer: Unlabeled data is raw data that does not have any tags or predefined output values associated with it.
Q7. What is a training dataset?
Answer: A training dataset is a collection of labeled examples used to teach an AI or ML model to recognize patterns and learn relationships.
Q8. What is a testing dataset?
Answer: A testing dataset is used to evaluate the accuracy and performance of a trained model using data not seen during training.
Q9. What is object classification?
Answer: Object classification is the process of identifying and categorizing objects in an image or dataset into predefined classes.
Q10. What is anomaly detection?
Answer: Anomaly detection is the process of identifying unusual patterns or values in data that differ significantly from normal behavior.
Section D: Long Answer Questions
(Answer in at least 80 words each)
Q1. Explain Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning and Deep Learning. Also describe the relationship among them with suitable examples.
Answer: Artificial Intelligence refers to the ability of machines to perform tasks that normally require human intelligence such as reasoning, learning and decision-making. Machine Learning is a subset of AI in which machines learn from data and improve their performance through experience without explicit programming. Deep Learning is a further subset of Machine Learning that uses artificial neural networks with multiple layers. For example, chatbots are AI applications, recommendation systems use Machine Learning, and image recognition systems use Deep Learning. Thus, AI is the broadest field, followed by ML and then DL.
Q2. Differentiate between Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning and Deep Learning on the basis of scope, data requirement and applications.
Answer: Artificial Intelligence is a broad concept that focuses on creating machines capable of performing human-like tasks such as reasoning and problem-solving. Machine Learning is a subset of AI that allows systems to learn patterns from data and improve performance over time. Deep Learning is a subset of ML that uses multi-layered neural networks to learn complex patterns. AI can work with limited data using rules, ML requires structured data, while DL needs large volumes of data. AI is used in chatbots, ML in recommendation systems and DL in image and speech recognition.
Q3. Explain the working of a Machine Learning model with the help of input, learning process and output.
Answer: A Machine Learning model works by taking historical or past data as input. This data is analyzed by the model to identify patterns and relationships. During the learning process, the model adjusts itself based on correct and incorrect predictions. Once trained, the model generates output or predictions for new data. For example, a model trained with labeled images of apples and strawberries learns their features and correctly classifies new fruit images. Over time, the model improves its accuracy with more data.
Q4. Differentiate between training dataset and testing dataset with the help of a real-life example.
Answer: A training dataset is used to teach the Machine Learning model by providing labeled data. It helps the model learn patterns and relationships in the data. On the other hand, a testing dataset is used to evaluate the accuracy and performance of the trained model using unseen data. For example, when a teacher teaches a chapter using examples, it is like training data. When a test is conducted to check students’ understanding, it acts like testing data.
Q5. Explain the terms data, features and labels. Differentiate between labeled and unlabeled data using an example.
Answer: Data refers to information collected in any form for analysis. Features are the input attributes or columns in a dataset, such as color and size. Labels are the output values the model predicts, such as fruit name. Labeled data has predefined tags or outputs attached to it, while unlabeled data does not have any tags. For example, images tagged as “apple” or “banana” are labeled data, whereas random fruit images without names are unlabeled data.
Class 10 Artificial Intelligence Code 417 – Notes and Worksheets
| Topics | Video Link | Notes, Worksheet & QnA |
|---|---|---|
| 1.1 AI Project Cycle | Watch Video | Notes, Worksheet & QnA |
| 1.2 Introduction to AI Domains | Watch Video | Notes, Worksheet & QnA |
| 1.3 Ethical Frameworks of AI | Watch Video | Notes, Worksheet & QnA |
By Anjeev Kr Singh – Computer Science Educator
Published on : January 17, 2026 | Updated on : January 17, 2026