Class 10 AI Code 417 Unit 2 Advanced Concepts of Modelling in AI – Deep Learning Notes with Worksheet

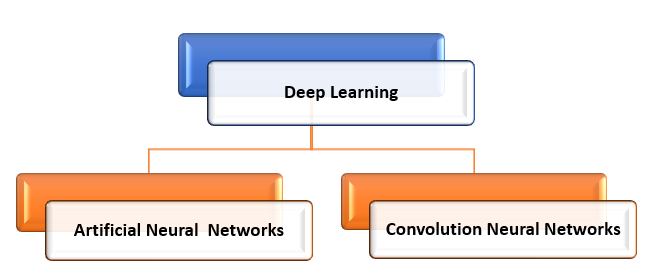
Deep Learning (DL)
Deep Learning enables software to train itself to perform tasks with vast amounts of data.
In deep learning, the machine is trained with huge amounts of data which helps it to train itself around the data.
Such machines are intelligent enough to develop algorithms for themselves.
Sub categories of Deep Learning
There are two types of Deep Learning models:
a) Artificial Neural Networks (ANN), and
b) Convolution Neural Network (CNN).
(a) Artificial Neural networks (ANN) –
Artificial Neural networks are modelled on the human brain and nervous system. They are able to automatically extract features without input from the programmer. Every neural network node is essentially a machine learning algorithm. It is useful when solving problems for which the data set is very large.
What is a Neural Network?
Neural networks are loosely modelled after how neurons in the human brain behave.
The key advantage of neural networks is that they are able to extract data features automatically without needing the input of the programmer.
A neural network is essentially a system of organizing machine learning algorithms to perform certain tasks. It is a fast and efficient way to solve problems for which the dataset is very large, such as in images.
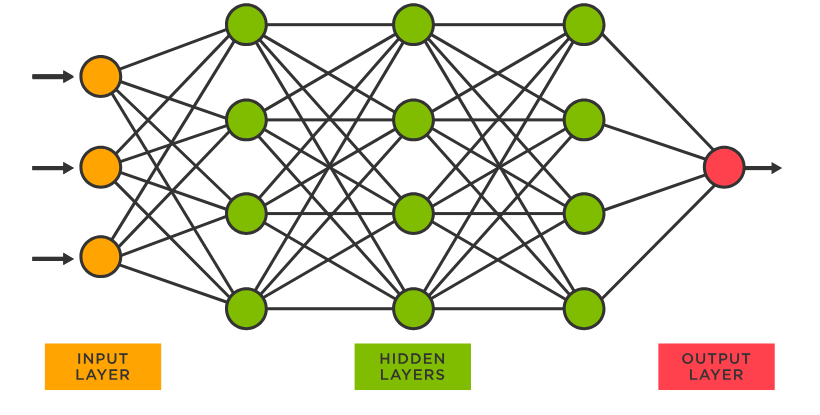
How neural networks work:
An artificial neural network is a type of machine learning algorithm derived from biological neural network principles that can work similarly to the human brain using neuron interconnection. These neurons are known as nodes.
- A Neural Network is divided into multiple layers and each layer is further divided into several blocks called nodes. Each node has its own task to accomplish which is then passed to the next layer.
- Neural Network consists of an input layer, hidden layer which performs computation using weights and biases on each node and finally, information is passed through these layers to reach the output layer.
- The first layer of a Neural Network is known as the input layer. The job of an input layer is to acquire data and feed it to the Neural Network. No processing occurs at the input layer.
- Next to it, are the hidden layers. Hidden layers are the layers in which the whole processing occurs. Their name essentially means that these layers are hidden and are not visible to the user. Each node of these hidden layers has its own machine learning algorithm which it executes on the data received from the input layer.
- The hidden layer performs computation by means of weights and biases Information passes from one layer to the other after the value found from this calculation passes through a selected activation function.
- The process of finding the right output begins with trial and error until the network finally learns.
- With each try, the weights are adjusted based on the error found between the desired output and the network output.
There can be multiple hidden layers in a neural network system and their number depends upon the complexity of the function for which the network has been configured.
Also, the number of nodes in each layer can vary accordingly. The last hidden layer passes the final processed data to the output layer which then gives it to the user as the final output.
Similar to the input layer, the output layer too does not process the data which it acquires. It is meant for user-interface.
Working of a Neural Network
Imagine each node as a simple calculator. It takes input numbers, multiplies them by certain values (weights), adds them together, adds an extra number (bias), and then gives an output. This output is used as input for the next node in the network. The formula would look something like this:
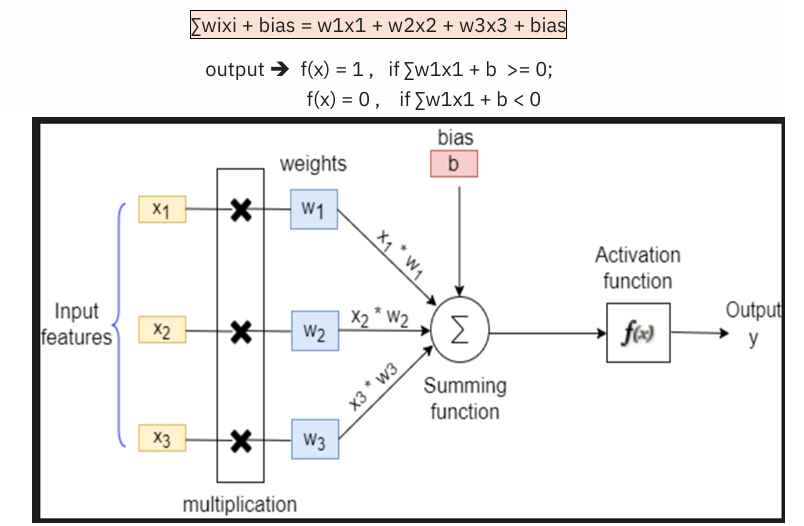
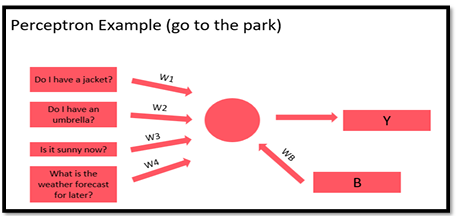
Case: You want to go out to the park today.
You can consider the following factors that may influence your decision
- Do I have a jacket?
- Do I have an umbrella?
- Is it sunny now?
- What is the weather forecast for later?
Note:
- All factors having equal value.
- The threshold is 8. If the result is above 8, you go ahead; if it’s below 8, you don’t.
- The value of Bias is 4.0.
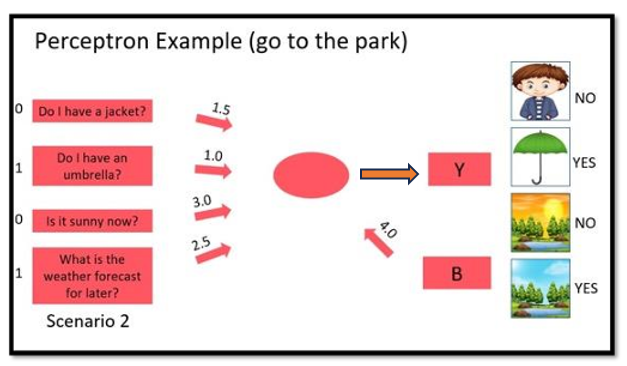
Let’s say: I have a jacket, I don’t have an umbrella, it is sunny now, and the weather forecast is going to rain. We can convert the yes and no to numbers 1 and 0.

Output = 1 x 1.5 + 0 x 1.0 + 1 x 3.0 + 0 x 2.5 + 4.0 = 8.5
From this calculation, the output is 8.5. Since this is higher than the threshold (which is 8.0), the result is I will go out to the park.
Now let us change for another example.
Let’s say: I don’t have a jacket, I have an umbrella, it is not sunny now, and the weather forecast is ok. We will convert the yes and no to numbers 1 and 0.
Output = 0 x 1.5 + 1 x 1.0 + 0 x 3.0 + 1 x 2.5 + 4.0 = 7.5
From this calculation, the output is 7.5. Since this is lower than the threshold (which is 8.0), the result is I will not go out to the park.
Application of ANN
- Real-world applications of neural networks are facial recognition, customer support chatbot, vegetable price prediction etc.
Neural network Game: https://playground.tensorflow.org/
b) Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)
Convolutional Neural Network is a Deep Learning algorithm which can take in an input image, assign importance (learnable weights and biases) to various aspects/objects in the image and be able to differentiate one from the other.
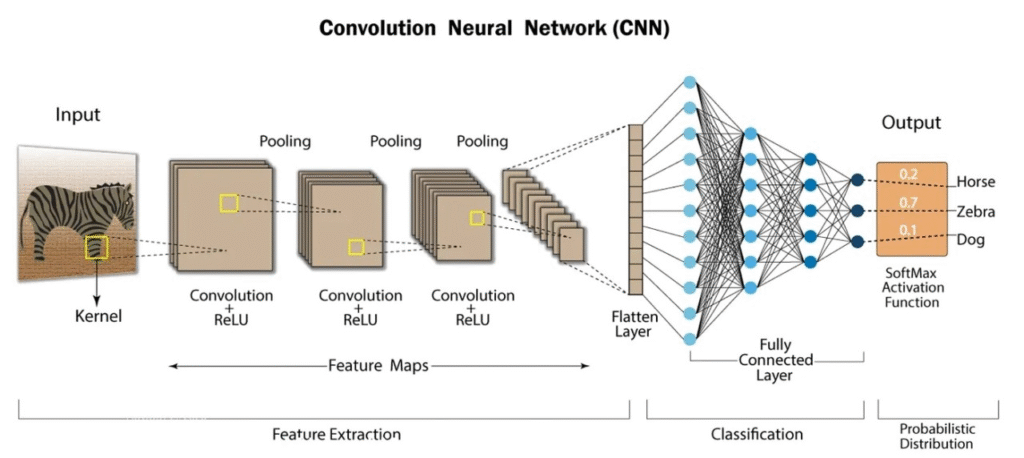
What is CNN?
A Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) is a type of Deep Learning algorithm mainly used for analyzing visual data such as images and videos.
Unlike traditional neural networks, CNNs can automatically detect important features (like edges, shapes, colors, textures, or even complex objects) without the need for manual feature extraction.
Key Concepts in CNN
- Input Layer
- The CNN takes an image as input, usually represented as a 2D matrix of pixel values.
- For colored images (RGB), it has 3 channels (Red, Green, Blue).
- Convolutional Layer
- This is the core building block of CNNs.
- It uses filters (kernels) that slide over the image and perform a convolution operation.
- The filters detect features like edges, corners, textures, etc.
- Each filter produces a feature map highlighting where that pattern appears.
- ReLU (Rectified Linear Unit) Activation
- Introduces non-linearity into the model.
- It replaces negative values with zero while keeping positive values.
- Pooling Layer (Downsampling/Subsampling)
- Reduces the spatial size of feature maps → lowers computation.
- Max Pooling is common: takes the maximum value in each region.
- Helps CNNs become translation invariant (e.g., detecting an object anywhere in an image).
- Fully Connected (FC) Layer
- After several convolution and pooling layers, the feature maps are flattened into a 1D vector.
- Connected to a fully connected layer (like traditional neural networks).
- Combines features to classify the image into categories.
- Output Layer
- Uses an activation function like Softmax (for multi-class classification).
- Produces probabilities for each class (e.g., “cat = 95%, dog = 4%, car = 1%”).
Why are CNNs Powerful?
- Automatic Feature Extraction → No need for manual feature engineering.
- Translation Invariance → Detects objects regardless of position.
- Parameter Sharing → A single filter is applied across the image, reducing computation.
- Hierarchical Feature Learning → Early layers detect simple patterns (edges, textures), deeper layers detect complex patterns (faces, objects).
Applications of CNN
- Image Recognition (e.g., facial recognition, handwriting recognition).
- Object Detection (e.g., self-driving cars detecting pedestrians).
- Medical Imaging (e.g., tumor detection in MRI scans).
- Video Analysis (e.g., action recognition, video surveillance).
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) (e.g., text classification with CNNs applied to word embeddings).
Deep Learning (DL) Worksheet – ANN & CNN (With Answers)
Section A: Multiple Choice Questions
- Deep Learning is a subset of
a) Database
b) Machine Learning
c) Networking
d) Cyber Security
Answer: b) Machine Learning - Artificial Neural Networks are inspired by the
a) CPU
b) Internet
c) Human Brain
d) Calculator
Answer: c) Human Brain - The first layer of a neural network is called the
a) Hidden layer
b) Output layer
c) Input layer
d) Pooling layer
Answer: c) Input layer - Most of the computation in a neural network occurs in the
a) Input layer
b) Hidden layer
c) Output layer
d) Dataset
Answer: b) Hidden layer - Weights and bias are used for
a) Storage
b) Visualization
c) Computation
d) Printing
Answer: c) Computation - Convolutional Neural Network is mainly used for
a) Audio processing
b) Image processing
c) Spreadsheet tasks
d) Typing
Answer: b) Image processing - Filters in CNN help in detecting
a) Passwords
b) Pixels only
c) Features like edges and shapes
d) Storage blocks
Answer: c) Features like edges and shapes - ReLU stands for
a) Random Linear Unit
b) Rectified Linear Unit
c) Repeated Learning Unit
d) Reduced Layer Unit
Answer: b) Rectified Linear Unit - The pooling layer mainly helps to
a) Increase image size
b) Reduce computation
c) Store data
d) Encrypt data
Answer: b) Reduce computation - Max pooling selects the
a) Minimum value
b) Average value
c) Maximum value
d) Random value
Answer: c) Maximum value - The final layer of CNN generally uses
a) Pooling
b) Convolution
c) Softmax
d) ReLU
Answer: c) Softmax - ANN performs best when the dataset is
a) Small
b) Medium
c) Very large
d) Empty
Answer: c) Very large - Bias is added to neurons to
a) Remove error
b) Adjust output
c) Store values
d) Delete nodes
Answer: b) Adjust output - Flattening is done before the
a) Input layer
b) Pooling layer
c) Fully connected layer
d) Activation layer
Answer: c) Fully connected layer - Facial recognition systems mostly use
a) ANN only
b) CNN
c) Excel
d) DBMS
Answer: b) CNN
Section B: Assertion and Reason
- Assertion: CNNs are widely used in image recognition. Reason: CNNs can automatically detect visual features like edges and shapes.
Answer: Both are true and the Reason correctly explains the Assertion. - Assertion: Input layer performs heavy computation. Reason: Input layer only accepts data.
Answer: Assertion is false and Reason is true. - Assertion: Hidden layers use weights and biases. Reason: Hidden layers process information.
Answer: Both are true and the Reason correctly explains the Assertion. - Assertion: Pooling layer increases image resolution. Reason: Pooling reduces feature map size.
Answer: Assertion is false and Reason is true. - Assertion: ANN always requires manual feature extraction. Reason: ANN can automatically extract features.
Answer: Assertion is false and Reason is true.
Section C: Fill in the Blanks
- Deep Learning is a subset of __________.
Answer: Machine Learning - ANN stands for __________.
Answer: Artificial Neural Network - CNN mainly processes __________ data.
Answer: image - The first layer is called the __________ layer.
Answer: input - The layer that performs computation is the __________ layer.
Answer: hidden - ReLU removes __________ values.
Answer: negative - Pooling reduces the __________ size of feature maps.
Answer: spatial - The final classification is done by the __________ layer.
Answer: output - Nodes in neural networks are also called __________.
Answer: neurons - Softmax provides __________ for each class.
Answer: probabilities
Section D: Short Answer Questions (30 words)
- What is Deep Learning?
Answer: Deep Learning is a machine learning technique that uses multi-layer neural networks to automatically learn patterns and features from large amounts of data. - What is an Artificial Neural Network?
Answer: An Artificial Neural Network is a brain-inspired computational model made of interconnected neurons that process information using weights, bias, and activation functions. - What is the role of hidden layers?
Answer: Hidden layers perform calculations, process inputs, and extract important features to help the network make accurate predictions. - Explain weights and bias.
Answer: Weights determine the importance of inputs, while bias shifts the output value to improve accuracy and learning. - What is CNN?
Answer: CNN is a deep learning algorithm designed to analyze images and visual data by automatically detecting patterns and features. - What is pooling?
Answer: Pooling is a technique used in CNN to reduce the size of feature maps, which decreases computation and improves efficiency. - Give two applications of ANN.
Answer: Facial recognition systems and customer support chatbots. - Give two applications of CNN.
Answer: Object detection in self-driving cars and medical image diagnosis.
Section E: Long Answer Questions (80 words)
- Explain the structure and working of an ANN.
Answer: An Artificial Neural Network consists of an input layer, one or more hidden layers, and an output layer. The input layer receives data, hidden layers perform computations using weights, bias, and activation functions, and the output layer produces the result. During training, the network adjusts weights based on errors using backpropagation, which helps the model learn patterns and improve accuracy. - Describe the working of CNN.
Answer: CNN processes images using convolution layers to extract features like edges and textures. ReLU introduces non-linearity, pooling reduces feature map size, and fully connected layers classify the image. The network automatically learns simple to complex patterns, making it very effective for visual recognition tasks. - Differentiate between ANN and CNN.
Answer: ANN is used for general data and has fully connected layers, while CNN is designed for image data using convolution and pooling layers. CNN automatically extracts spatial features and requires fewer parameters compared to ANN. - Explain weights, bias, and activation function with example.
Answer: Weights multiply inputs to decide importance, bias shifts the result, and activation functions introduce non-linearity. For example, a neuron multiplies inputs with weights, adds bias, and passes the result through ReLU to produce output. - Explain applications of Deep Learning.
Answer: Deep Learning is used in facial recognition, speech recognition, medical diagnosis, recommendation systems, autonomous vehicles, chatbots, and video surveillance. It helps machines learn automatically from large datasets.
Section F: Competency / Case-Based Questions
- A company wants to detect faces from CCTV footage. Which model should be used and why?
Answer: CNN should be used because it automatically detects visual features and patterns in images, making it ideal for face detection. - A student uses ANN with very few hidden layers and gets poor accuracy. What could be the reason?
Answer: The network may be underfitting because it lacks enough layers to learn complex patterns. - During training, negative values are removed using a function. Name the function and its purpose.
Answer: ReLU activation function removes negative values and introduces non-linearity to improve learning. - A CNN model is taking too much computation time. Which layer can reduce computation and how?
Answer: The pooling layer reduces feature map size, which decreases computation and speeds up processing. - A neural network improves output after many attempts. Which learning concept is used?
Answer: The network uses trial-and-error learning through backpropagation to adjust weights and reduce errors.
By Anjeev Kr Singh – Computer Science Educator
Published on : February 4, 2026 | Updated on : February 4, 2026