Session 1 Fundamentals of Computer XI IT 802 Book Solution

Unit 1 – Computer Organisation Session 1 Fundamentals of Computer
Self Assessment Exercises
1. Define the following :
a. Computer b. Input Device
c. Output Device d. Processor
Answer:
- (a) Computer: Computer is a term derived from the term ‘compute’ which means to calculate. Computer is an electronic device which takes input from the user, processes the input according to the set of instructions and gives the output. It is a device that works on a set of instructions.
- (b) Input Device: Input device is responsible to take data & instructions as input from the user, translate it in machine code and send to the CPU for further processing.
Example of Input devices are – Keyboard, Mouse, Touch Screen, MICR, OCR, Scanner, Mic, etc. - (c) Output Device: Output device is responsible to take the information from the CPU, translate in human understanding form, and gives to the user.
Example of Output devices are – Monitor, Printer, Speaker, Plotter, etc. - (d) Processor: Processor is a device which is also known as Microprocessor or CPU (Central Processor Unit). Processor is responsible to perform all processing upon the data as per the instructions given by user. CPU has two sub units known as Control Unit (CU) and Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU).
2. Expand the following :
a. ALU b. CPU c. CU d. RAM
e. EEPROM f. ROM g. DRAM h. SDRAM
Answer:
- a. ALU: Arithmetic and Logic Unit
- b. CPU: Central Processing Unit
- c. CU: Control Unit
- d. RAM: Random Access Memory
- e. EEPROM: Electronic Erasable Read Only Memory
- f. ROM: Read Only Memory
- g. DRAM: Dynamic Random Access Memory
- h. SDRAM: Static Dynamic Random Access Memory
3. Answer the following
a. Explain the block diagram of computer.
Answer: Block diagram of computer shows that there are four important units of a computer system. These are –
(1) Input Unit
(2) Storage Unit
(3) Central Processing Unit
(4) Output Unit.
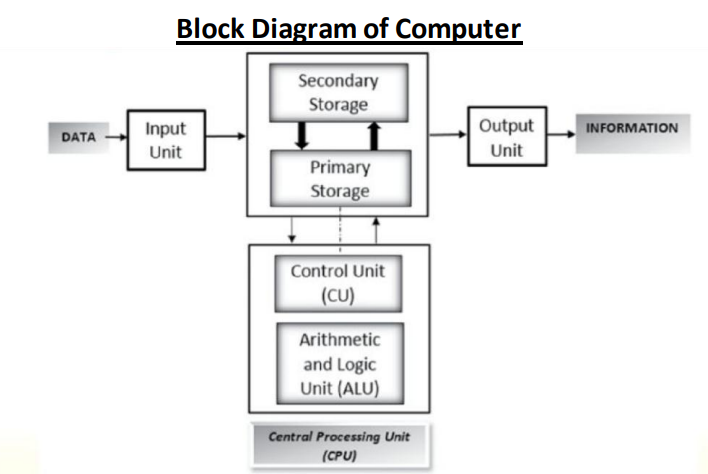
- Input unit is responsible to take data and instructions from user and send it to the storage unit i.e. primary memory for processing.
- After this control unit instruct the ALU to perform the Arithmetic and Logical calculation as per the instructions given by user.
- After processing ALU send the result to the primary memory and then CU instruct the output unit to display the result.
b. Describe the function of ALU and CU in short.
Answer: Central Processing Unit is divided in to the two sub units known as – ALU and CU.
- Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU) is responsible to perform the two types of calculations. Arithmetical calculation which means simple addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. Logical calculation means performing the comparision between two values and gives the result as True or False.
- Control Unit (CU) is the main unit of computer system, which is responsible to control all other units. CU gives the control signal to all units to perform their task.
c. Differentiate between RAM and ROM.
Answer: RAM vs ROM
| RAM | ROM |
| Random Access Memory | Read Only Memory |
| It is a volatile memory i.e., its data gets lost once the power supply is stopped. | It is non-volatile memory i.e. its data does not gets lost once the power supply is stopped. |
d. Differentiate between input and output devices.
Answer: Input Device vs Output Device
| Input Device | Output Device |
| Input Device is responsible to take input from the user. | Output Device is responsible to to give results to the user. |
| Example: Keyboard, Mouse, Scanner, Mic, MICR, etc. | Example: Monitor, Printer, Speaker, Plotter, etc. |
By Anjeev Kr Singh – Computer Science Educator
Published on : August 7, 2025 | Updated on : August 9, 2025


