Ethical Frameworks for AI: Class 10 Notes, Worksheet & Answers
Frameworks
Frameworks are a set of steps that help us in solving problems. It provides a step-by-step guide for solving problems in an organized manner.
- Frameworks offer a structured approach to problem-solving, ensuring that all relevant factors and considerations are taken into account.
- Additionally, they serve as a common language for communication and collaboration, facilitating the sharing of best practices and promoting consistency in problem- solving methodologies.
- Example: AI Project Cycle
Ethical Frameworks
Ethics: Ethics are a set of values or morals that help us separate right from wrong.
Ethical frameworks are frameworks which help us ensure that the choices we make do not cause unintended harm.
- Ethical frameworks provide a systematic approach to navigating complex moral dilemmas by considering various ethical principles and perspectives.
- By utilizing ethical frameworks, individuals and organizations can make well-informed decisions that align with their values and promote positive outcomes for all stakeholders involved.
Why do we need Ethical Frameworks for AI?
- As we have seen how bias could result in unwanted outcomes in AI solutions.
- Think of the hiring algorithm which was biased against women applicants!
- AI is essentially being used as a decision-making/ influencing tool. As such we need to ensure that AI makes morally acceptable recommendations
- Ethical frameworks ensure that AI makes morally acceptable choices. If we use ethical frameworks while building our AI solutions, we can avoid unintended outcomes, even before they take place!
Benefits of Ethical Frameworks
We need ethical frameworks for AI to ensure that AI systems are developed and used responsibly, safely, and fairly. These frameworks help prevent harm, protect human rights, ensure accountability, and promote trust in AI technologies.
- Prevent Harm – To avoid misuse and minimize risks like discrimination, bias, or privacy violations.
- Ensure Fairness – To promote equality and prevent unfair treatment by AI systems.
- Protect Human Rights – To safeguard individual rights such as freedom, dignity, and consent.
- Promote Transparency & Accountability – To make AI decisions understandable and hold creators responsible.
- Build Trust – To increase public confidence in using AI safely and ethically.
Activity 1: My Goodness – https://www.my-goodness.net/
- Purpose: To understand how our decisions get influenced by our personal morals, values and ethics!
- Say: “Carefully read the descriptions provided that help you decide on donating. Explore your decision-making ability.”
- Visit the website – https://www.my-goodness.net/
- Take a quick look at the video to learn more about the game!
- Players must make 10 decisions on how they would like to make a charitable donation. In most cases, players will receive details about the recipients. They will also be given information on the intended use of the money they are donating.
- In a few instances, this may be hidden from them, however they can choose to reveal it. This activity aims to understand an individual’s judgment. We are looking to discover potential biases within us!
- Data is collected anonymously and with your consent. If you wish to delve deeper and explore your own decision-making, click on “yes.”

- After clicking on “yes” you will be taken to a short survey. After the survey has been filled, you will see interesting insights about your decisions.
Question Time ?
- Did you discover any internal biases in your decisions?
- Do you agree with the results shared by the game?
Factors that could influence your decisions without you realizing it include
- Identity of the charity recipient.
- Location of the recipient.
- Bias towards relatives.
- Uncovering information available.
This is just an exercise to uncover our biases and thought processes behind making certain decisions. This will help us in producing a framework which can aid in making decisions which are ethically sounder.
Factors Influence our decision-making:
- Emotions – Feelings like fear, joy, or anger can influence decisions.
- Past Experiences – Previous outcomes help guide current choices.
- Social Influence – Family, peers, and societal norms shape our thinking.
- Religion and Beliefs – Faith and moral teachings affect what we consider right or wrong.
- Cognitive Biases – Mental shortcuts can lead to irrational or flawed decisions.
- Intuition and Personal Values – Gut feelings and deeply held values often guide us, especially in complex or moral decisions.
Types of Ethical Frameworks
Ethical frameworks for AI can be categorized into two main types:
- Sector – based framework and
- Value – based framework.
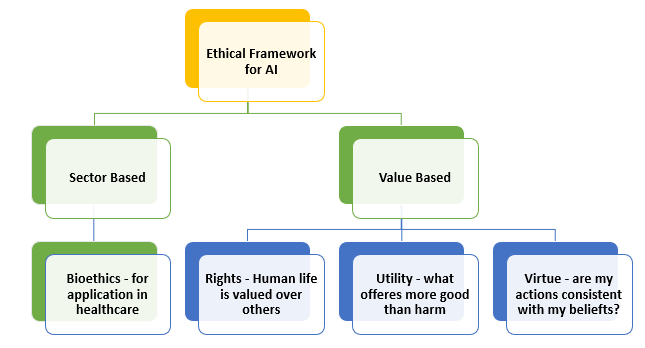
1. Sector-based Frameworks
- These are frameworks tailored to specific sectors or industries.
- In the context of AI, one common sector-based framework is Bioethics, which focuses on ethical considerations in healthcare. It addresses issues such as patient privacy, data security, and the ethical use of AI in medical decision-making.
- Sector-based ethical frameworks may also apply to domains such as finance, education, transportation, agriculture, governance, and law enforcement.
2. Value-based Frameworks:
- Value-based frameworks focus on fundamental ethical principles and values guiding decision- making.
- It reflects the different moral philosophies that inform ethical reasoning.
- Value-based frameworks are concerned with assessing the moral worth of actions and guiding ethical behaviour.
- They can be further classified into three categories:
- Rights-based:
- Prioritizes the protection of human rights and dignity, valuing human life over other considerations.
- It emphasizes the importance of respecting individual autonomy, dignity, and freedoms.
- In the context of AI, this could involve ensuring that AI systems do not violate human rights or discriminate against certain groups.
- Utility-based:
- Evaluates actions based on the principle of maximizing utility or overall good, aiming to achieve outcomes that offer the greatest benefit and minimize harm.
- It seeks to maximize overall utility or benefit for the greatest number of people.
- In AI, this might involve weighing the potential benefits of AI applications against the risks they pose to society, such as job displacement or privacy concerns.
- Virtue-based:
- This framework focuses on the character and intentions of the individuals involved in decision-making.
- It asks whether the actions of individuals or organizations align with virtuous principles such as honesty, compassion, and integrity.
- In the context of AI, virtue ethics could involve considering whether developers, users, and regulators uphold ethical values throughout the AI lifecycle.
Benefits of classifications of Ethical Frameworks:
These classifications
- provides a structured approach for addressing ethical concerns in AI development and deployment,
- ensuring that considerations relevant to specific sectors and
- Fundamental ethical values are adequately addressed.
Bioethics
- Bioethics is an ethical framework used in healthcare and life sciences.
- It deals with ethical issues related to health, medicine, and biological sciences, ensuring that AI applications in healthcare adhere to ethical standards and considerations.
Principles of bioethics:
- Respect for Autonomy – Acknowledge and support individuals’ rights to make their own informed decisions.
- Do Not Harm (Non-maleficence) – Avoid causing physical, emotional, or psychological harm to others.
- Ensure Maximum Benefit for All (Beneficence) – Act in ways that promote the well-being and best interests of individuals and society.
- Give Justice – Treat people fairly and ensure equal access to resources, care, and opportunities.
Note:
- Non-maleficence: refers to the ethical principle of avoiding causing harm or negative consequences. It emphasizes the obligation to minimize harm as much as possible and prioritize actions that prevent harm to individuals, communities, or the environment.
- Maleficence: refers to the concept of intentionally causing harm or wrongdoing.
- Beneficence: refers to the ethical principle of promoting and maximizing the well-being and welfare of individuals and society. It emphasizes taking actions that produce positive outcomes and contribute to the overall good, ensuring that the greatest benefit is achieved for all stakeholders involved.
Case Study: Impact of the application of an AI ethical framework on the end outcome
- Aim: A company aimed to support hospitals in optimizing patient care by creating an AI algorithm designed to identify individuals at high risk.
- Objective:
The objective was to provide healthcare providers with valuable insights to allocate resources effectively and ensure those most in need receive appropriate attention. - Consequences:
However, potential unintended consequences lead to some problems in the model, such as the algorithm inadvertently exacerbating existing biases or inaccuracies in the data, potentially leading to misclassification of patients or overlooking critical cases.
Addressing concerns about the algorithm’s accuracy and reliability becomes paramount, as any flaws in its design or training data could compromise patient care and outcomes.
The problem it caused:
Patients from the Western region of a particular area, who were categorized at the same risk level by the algorithm, generally exhibited more severe health conditions compared to patients from other regions.
Why does the problem happen?
- The algorithm utilized was trained on healthcare expense data as a measure for health metrics rather than actual physical illness.
- This algorithm was created in the United States where less money is spent on western region patient healthcare than other ethnic patient healthcare.
Solution of the above Health Problem:
Use principles of the Bioethics framework to ensure an ethical AI solution. The four principles of bioethics can be used to ensure an ethical AI solution for the healthcare problem.
i. Respect for autonomy: Enabling users to be fully aware of decision-making. E.g., users of an AI algorithm should know how it functions.
- The data that models were trained on, and used to make decisions, should be reproducible and accessible to the patients.
- In the event of performance concerns, model predictions and data labels should be released.
ii. Do not harm: Harm to anyone (be it human or non–human) must be avoided at all costs. If no choice is available, the path of least harm must be always chosen.
- Promote well-being, minimize harm, and ensure that benefits and harms are distributed among stakeholders in a just manner.
- The AI algorithm must be trained on data sets that equitably reduce harm for all, not just harm for some groups.
- In this instance, patients from other regions excluding western part who were less ill would receive more intensive care from doctors than patients who actually require help.
- This algorithm, if implemented, would actively harm patients belong to western region by inappropriately recommending healthcare resource allocation.
iii. Maximum benefit: Not only should we avoid harm, our actions must focus on providing the maximum benefit possible.
- The solution should be held to clinical practice standards, not merely technological ethics standards.
- It should go beyond nonmaleficence and strive for beneficence.
- Considering the example we discussed, the AI algorithm should not only avoid causing harm to patients from the western region but also provide benefits to these patients, as well as patients from other regions and of all races.
- Is there a better data set for training that reflects the healthcare needs and outcomes of patients of all races?
- The data we use for training must be unbiased.
iv. Justice: All benefits and burdens of a particular choice must be distributed in a justified manner across people irrespective of their background.
- Solution development requires concerted and in-depth knowledge of social structures at play that result in issues like racism and sexism (a few types of societal biases).
- The solution needs to be aware of social determinants of healthcare and actively work against those structures.
We saw that abiding by bioethical principles could have helped us to avoid the unintended consequences of the AI solution.
WORKSHEET: Ethical Frameworks for AI
A. Multiple Choice Questions (20 MCQs)
- What is a framework?
A. A computer program
B. A set of moral rules
C. A step-by-step guide to solve problems
D. A type of AI model
Ans: C - Ethical frameworks help in:
A. Speeding up AI models
B. Avoiding unintended harm
C. Increasing profits
D. Replacing humans
Ans: B - Ethics refers to:
A. Legal rules
B. Technical standards
C. Values that distinguish right from wrong
D. Computer instructions
Ans: C - Why are ethical frameworks needed for AI?
A. AI works slowly
B. AI can show bias
C. AI uses electricity
D. AI replaces jobs
Ans: B - AI is mainly used as a:
A. Storage tool
B. Gaming system
C. Decision-making tool
D. Communication device
Ans: C - Which of the following is NOT a benefit of ethical frameworks?
A. Prevent harm
B. Ensure fairness
C. Increase bias
D. Build trust
Ans: C - Which activity helps uncover personal biases?
A. AI Project Cycle
B. My Goodness game
C. Python coding
D. Data labeling
Ans: B - Data in the “My Goodness” activity is collected:
A. Publicly
B. Without consent
C. Anonymously
D. For marketing
Ans: C - Which factor can influence decisions unconsciously?
A. Programming language
B. Emotions
C. Storage size
D. Internet speed
Ans: B - Ethical frameworks are mainly classified into:
A. Two types
B. Three types
C. Four types
D. Five types
Ans: A - Sector-based frameworks are designed for:
A. Moral philosophy
B. Specific industries
C. All AI models
D. Programming ethics
Ans: B - Bioethics is mainly related to:
A. Education
B. Finance
C. Healthcare
D. Agriculture
Ans: C - Which is NOT a value-based ethical framework?
A. Rights-based
B. Utility-based
C. Sector-based
D. Virtue-based
Ans: C - Rights-based ethics emphasizes:
A. Maximum profit
B. Human dignity and rights
C. Speed
D. Automation
Ans: B - Utility-based ethics focuses on:
A. Intentions
B. Individual rights
C. Maximum overall benefit
D. Laws
Ans: C - Virtue-based ethics evaluates:
A. Outcomes
B. Character and intentions
C. Data accuracy
D. Speed
Ans: B - Which principle means “do no harm”?
A. Justice
B. Autonomy
C. Beneficence
D. Non-maleficence
Ans: D - Beneficence means:
A. Avoiding harm
B. Promoting well-being
C. Equal distribution
D. Data privacy
Ans: B - The healthcare AI problem occurred due to use of:
A. Physical illness data
B. Genetic data
C. Healthcare expense data
D. Survey data
Ans: C - Justice in bioethics ensures:
A. Faster AI
B. Fair distribution of benefits and burdens
C. Maximum profit
D. Automation
Ans: B
B. Fill in the Blanks (5)
- Ethics help us differentiate between right and wrong.
- Ethical frameworks prevent unintended harm in AI systems.
- Bioethics is a sector-based ethical framework.
- Non-maleficence means avoiding harm.
- The AI healthcare issue was caused due to biased training data.
C. True / False (5)
- Ethical frameworks help increase bias in AI.
False - AI can influence important human decisions.
True - Utility-based ethics focuses on individual character.
False - Bioethics is mainly used in healthcare.
True - Justice ensures fair treatment for all individuals.
True
D. Short Answer Questions (6) – (20–30 words each)
- What is an ethical framework?
An ethical framework is a structured approach that guides decision-making to ensure actions are morally acceptable and do not cause unintended harm. - Why is AI bias dangerous?
AI bias can lead to unfair decisions, discrimination, and harm to certain groups, reducing trust and violating ethical and human rights principles. - What is sector-based ethical framework?
Sector-based frameworks are designed for specific industries like healthcare or finance, addressing ethical concerns unique to those domains. - Define non-maleficence.
Non-maleficence is the ethical principle that emphasizes avoiding harm and preventing negative consequences to individuals or society. - What does beneficence focus on?
Beneficence focuses on promoting well-being and maximizing positive outcomes for individuals and society. - How does transparency help ethical AI?
Transparency allows users to understand AI decisions, builds trust, and ensures accountability of developers and organizations.
E. Long Answer Questions (4) – (50–80 words each)
- Explain the need for ethical frameworks in AI.
Ethical frameworks are essential in AI to ensure systems are fair, safe, and responsible. Since AI influences critical decisions, ethical frameworks help prevent bias, discrimination, and harm. They protect human rights, promote transparency, ensure accountability, and build public trust in AI technologies. - Describe value-based ethical frameworks with examples.
Value-based ethical frameworks focus on moral principles guiding decision-making. Rights-based ethics protects human dignity and autonomy. Utility-based ethics aims to maximize overall benefit and minimize harm. Virtue-based ethics emphasizes moral character and intentions of developers and users throughout the AI lifecycle. - Explain the principles of bioethics.
Bioethics includes respect for autonomy, non-maleficence, beneficence, and justice. These principles ensure informed decision-making, avoidance of harm, promotion of well-being, and fair distribution of healthcare resources, especially when AI is used in medical systems. - How could bioethics prevent bias in healthcare AI systems?
Applying bioethical principles ensures AI models use unbiased data, avoid harm to specific groups, promote maximum benefit, and distribute resources fairly. Transparency and justice help identify social inequalities, preventing discrimination and improving patient outcomes across all regions and communities.
By Anjeev Kr Singh – Computer Science Educator
Published on : January 16, 2026 | Updated on : January 17, 2026