Class 10 AI Unit 2: Advanced Concepts of Modelling in AI – AI Modelling Notes with Practice Worksheet

2.2 AI Modelling
AI Modelling refers to developing algorithms, also called models, which can be trained to get intelligent outputs. That is, writing code to make a machine artificially intelligent.
AI modeling is the process of creating, training, and deploying a computer program or algorithm that is capable of learning from data to make decisions or predictions.
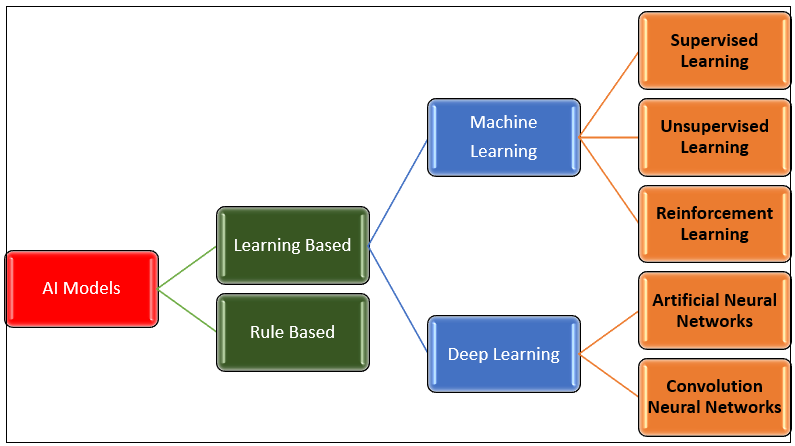
Types of AI Models
There are two types of AI Models –
(a) Rule Based Approach, and
(b) Learning Based Approach
Rule-Based Approach:
Rule Based Approach refers to the AI modelling where the relationship or patterns in data are defined by the developer.
The machine follows the rules or instructions mentioned by the developer and performs its task accordingly.
A rule-based approach is generally based on the data and rules fed to the machine, where the machine reacts accordingly to deliver the desired output.

A rule-based approach is a decision-making or problem-solving method that uses a predefined set of rules, often in the form of “IF-THEN” statements, to arrive at a conclusion or action.
Rule-based Chatbots are commonly used on websites to answer frequently asked questions (FAQs) or provide basic customer support.
How the Rule-Based Approach AI Model works:
- Data: The Chatbot doesn’t require a massive dataset for training. It relies on a predefined set of questions and corresponding answers.
- Rules: The Chatbot uses a decision tree approach with clearly defined rules to understand user queries and provide responses. Here’s a simplified example:
- Rule 1: If the user’s message contains keywords like “track order,” “shipment status,” or “delivery,” proceed to order tracking options.
- Rule 2: Under order tracking options:
- If the user asks for their order number, prompt them to enter it.
- If the user enters a valid order number, retrieve the tracking information from the database and display it.
- If the user enters an invalid order number, provide an error message and ask them to re-enter it.
- Rule 3: If the user’s message doesn’t match any defined rules, offer a message like “Sorry, I can’t help you with that. Perhaps you can try searching our FAQs or contacting customer support.”
- Interaction: When a user chats with the bot, their message is analyzed based on the defined rules. The Chabot responds with a pre-written answer or prompts the user for additional information depending on the scenario.
A drawback of Rule Based Approach:
- A drawback/feature for rule-based approach is that the learning is static.
- The machine, once trained, does not take into consideration any changes made in the original training dataset.
- That is, if you try testing the machine on a dataset that is different from the rules and data you fed it at the training stage, the machine will fail and will not learn from its mistake.
- Once trained, the model cannot improvise itself on the basis of feedback.
- Machine learning gets introduced as an extension to this as in that case, the machine adapts to changes in data and rules and follows the updated path only, while a rule-based model does what it has been taught once.
Learning Based Approach:
Under a Learning based approach, the machine is fed with data and the desired output to which the machine designs its own algorithm (or set of rules) to match the data to the desired output fed into the machine.

A learning-based approach is a method where a computer learns how to do something by looking at examples or getting feedback, similar to how we learn from experience.
Instead of being explicitly programmed for a task, the computer learns to perform it by analyzing data and finding patterns or rules on its own.
Learning based approach refers to AI modelling where the machine learns by itself.
- Under the Learning Based approach, the AI model gets trained on the data fed to it and then is able to design a model which is adaptive to the change in data.
- That is, if the model is trained with X type of data and the machine designs the algorithm around it, the model would modify itself according to the changes which occur in the data so that all the exceptions are handled in this case.
Example – Learning based Spam Email Filter
- A learning-based spam email filter is a computer program that automatically identifies whether an incoming email is spam or not. Instead of being explicitly programmed with rules for identifying spam, the filter learns from examples of labeled emails during a training phase.
- During training, the filter is provided with a large dataset of emails, each labeled as either spam or legitimate (non-spam).
- The filter analyzes the content and characteristics of these emails, such as words used, sender information, and presence of attachments.
- Using machine learning algorithms, the filter learns to recognize patterns that distinguish spam from legitimate emails.
- Once trained, the filter can classify new incoming emails as spam or not spam based on the patterns it learned. It continuously adapts and improves its accuracy over time as it encounters new examples.
- This learning-based approach allows the filter to effectively identify and filter out spam emails, helping users manage their email inbox more efficiently.
Categories of Learning based Model
Learning-based approaches are indeed a broad category that encompass both
- Machine learning and
- Deep learning.
Categories of Machine learning based models
Machine learning can further be divided into three parts:
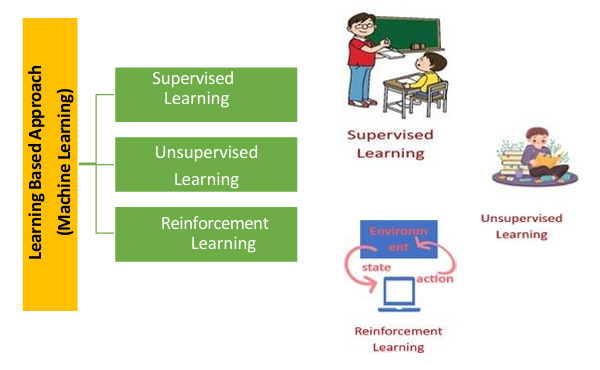
- Supervised Learning
- Classification b. Regression
- Unsupervised Learning
- Clustering b. Association
- Reinforcement Learning

- Supervised Learning
In a supervised learning model, the dataset which is fed to the machine is labelled.
In other words, we can say that the dataset is known to the person who is training the machine only then he/she is able to label the data.
A label is some information which can be used as a tag for data.
For example, students get grades according to the marks they secure in examinations. These grades are labels which categorize the students according to their marks.
- Supervised Learning indicates having a supervisor as a teacher.
- For e.g. A math teacher teaches the class by making the students learn using a lot of solved examples(training) and then test the knowledge gained by giving the class problems to solve on their own.
- Similarly, Supervised Learning is when you make the machine learn by teaching or training the machine using labeled data.
Supervised Learning – Examples
Example 1: Currency Coin
- Problem Statement: Build a model to predict the coin based on its weight.
- Assume that we have different currency coins (dataset) having different weights.
| Currency | Weight |
| 1 Euro | 5 grams |
| 1 Dirham | 7 grams |
| 1 Dollar | 3 grams |
| 1 Rupee | 4 grams |
- Feature – Weights
- Label – Currency
- So, if a model is trained in tagging the features i.e., the weights of the coin with the targets i.e., currency, the trained model can be further used to identify a coin based on its weight (since it has already learnt).
Example 2 – Supervised Machine Learning (using labelled data)

- In the example shown in the image, the model has learned from labeled input data and produces output to classify them as Carrot, Tomato & Bell Pepper.
- Therefore, you can see that the model learns from the training data and then applies the same knowledge to test data.
Sub-categories of Supervised Learning Model

There are two types of Supervised Learning models:
a) Classification model and
b) Regression model.
a) Classification Model:
- In classification, the data is classified according to the labels.
- The task of the classification algorithm is to assign an input value to a class or category based on the training data.
- For example,
- In the grading system, students are classified on the basis of the grades they obtain with respect to their marks in the examination.
- This model works on a discrete dataset which means the data need not be continuous.
Examples of the Classification Model

Classifying Weather is Hot or Cold:
- In this case, the model would be trained on historical weather data that includes temperature information labeled as “hot” or “cold”.
- The model would learn the patterns that differentiate hot and cold weather based on factors like:
- Location (average temperatures vary geographically)
- Season (summer vs. winter)
- High and low temperatures
- Humidity
- When presented with weather data for tomorrow, the trained classification model would analyze these factors and predict the most likely category – “hot” or “cold” weather tomorrow.
Classifying emails as spam or not:
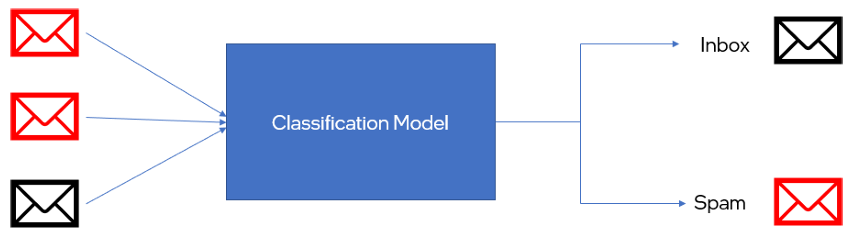
- In this case, the model would be trained on tons of emails, both real ones (like from friends or colleagues) and spam.
- The model learns what makes an email look like spam.
- Once trained, the model sees a new email. It analyzes the clues in the email and decides: is this spam or not? It assigns a category – “spam” or “not spam” – just like sorting your mail.
- In modern-day Email, classifiers identify if the email is spam and have evolved into other categories such as social, advertisement, notifications, etc. Similar models are increasingly being used in messaging applications.
b) Regression Model
- Regression models work on continuous data.
- For example,
- If you wish to predict your next salary, then you would put in the data of your previous salary, any increments, etc., and would train the model.
- Here, the data which has been fed to the machine is continuous.
- Regression algorithms predict a continuous value based on the input variables.
- Continuous values as Temperature, Price, Income, Age, etc.

Examples of the Regression Model
Example 1: Predicting temperature
- Temperature is a continuous variable, meaning it can take on any value within a range. Regression models are well-suited for predicting continuous outputs.
Example 2: Predicting the price of the house
- Predicting the price of the house based on some parameters:
- 1. Features/Independent Variables
- 1. No of bedrooms
- 2. Carpet Size
- 3. Garage Area
- 2. Label/Dependent Variable
- 1. Price [Label/Dependent Variable]
- 1. Features/Independent Variables
- In the House Price Prediction Problem, we are trying to predict the price (dependent variable) based on certain parameters like the number of bedrooms, carpet size, and garage area (independent variables).
Example 3: Used Car Price Prediction
- This model predicts the selling price of the car with the help of a few parameters like
- fuel type,
- years of service,
- the number of previous owners,
- kilometers driven,
- transmission type (manual/automatic)
- This type of model will be of type regression since it will predict an approximate price (continuous value) of the car based on the training dataset.
Test Your Learning
Identify the model: Classification or Regression?
- Case 1: Predicting whether a customer is eligible for a bank loan or not?
- Ans: It is Classification. Binary Classification; since the model is going to predict whether or not the customer is eligible for a loan- The output will be either yes or no (discrete values i.e. non-continuous data).
- Case 2: Predicting weather for next 24 hours
Ans: It is Regression because predicting weather for next 24 hours will be a continuous range (it will keep changing over the period of 24 hours).
| 2.1 Revisiting AI, ML, DL | Watch Video | Notes, Worksheet & QnA |
| 2.2 (a) AI Modelling – Rule-Based, Learning Based, Machine Learning, Supervised Learning | Watch Video | Notes, Worksheet & QnA |
Worksheet
Class 10 – Artificial Intelligence (Code 417)
Unit-2: Advanced Concepts of Modelling in AI (AI Modelling)
Section A: Multiple Choice Questions (15)
Q1. AI Modelling refers to:
a) Storing data in computers
b) Writing codes to make machines intelligent
c) Designing websites
d) Using only hardware
Answer: b) Writing codes to make machines intelligent
Q2. Which of the following is NOT a type of AI model?
a) Rule Based
b) Learning Based
c) Hardware Based
d) Machine Learning Based
Answer: c) Hardware Based
Q3. In a rule-based approach, rules are defined by:
a) Machine itself
b) Dataset
c) Developer
d) End user
Answer: c) Developer
Q4. Rule-based systems mainly use:
a) Neural networks
b) IF–THEN statements
c) Trial and error
d) Random guessing
Answer: b) IF–THEN statements
Q5. Rule-based chatbots are commonly used for:
a) Image recognition
b) FAQs and customer support
c) Self-driving cars
d) Speech translation
Answer: b) FAQs and customer support
Q6. A major drawback of rule-based AI is that it is:
a) Expensive
b) Adaptive
c) Static
d) Fast
Answer: c) Static
Q7. Learning-based models design rules by:
a) Fixed instructions
b) User commands
c) Learning from data
d) Internet access
Answer: c) Learning from data
Q8. Spam email filtering is an example of:
a) Rule-based AI
b) Learning-based AI
c) Robotics
d) Hardware AI
Answer: b) Learning-based AI
Q9. Learning-based models improve because they:
a) Ignore mistakes
b) Use fixed rules
c) Adapt to new data
d) Stop learning after training
Answer: c) Adapt to new data
Q10. Which approach does NOT require explicit programming of rules?
a) Rule-based
b) Learning-based
c) Decision tree
d) Static model
Answer: b) Learning-based
Q11. Supervised learning uses data that is:
a) Unlabeled
b) Random
c) Labeled
d) Encrypted
Answer: c) Labeled
Q12. Predicting whether an email is spam or not is an example of:
a) Regression
b) Clustering
c) Classification
d) Association
Answer: c) Classification
Q13. Regression models work on:
a) Discrete data
b) Continuous data
c) Text data
d) Boolean data
Answer: b) Continuous data
Q14. Predicting house price is an example of:
a) Classification
b) Clustering
c) Regression
d) Association
Answer: c) Regression
Q15. Which learning category includes classification and regression?
a) Reinforcement learning
b) Unsupervised learning
c) Supervised learning
d) Deep learning
Answer: c) Supervised learning
Assertion–Reason Questions
Q1. Assertion (A): Artificial Intelligence is a broader concept that includes Machine Learning and Deep Learning.
Reason (R): Machine Learning and Deep Learning are independent technologies that do not depend on Artificial Intelligence.
Answer: Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
Q2. Assertion (A): Deep Learning models require large amounts of data for effective training.
Reason (R): Deep Learning uses neural networks with multiple hidden layers to learn complex patterns.
Answer: Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
Q3. Assertion (A): Rule-based AI systems can improve their performance automatically with experience.
Reason (R): Rule-based AI systems follow predefined rules created by developers.
Answer: Assertion is false, but Reason is true.
Q4. Assertion (A): Supervised learning requires labeled data for training the model.
Reason (R): Labeled data helps the model compare its predictions with correct outputs and learn from errors.
Answer: Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
Q5. Assertion (A): Classification problems always produce numerical outputs.
Reason (R): Classification assigns input data into predefined categories or classes.
Answer: Assertion is false, but Reason is true.
Q6. Assertion (A): Regression is used when the output variable is continuous in nature.
Reason (R): Regression predicts exact numeric values such as temperature or price.
Answer: Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
Q7. Assertion (A): Unlabeled data is commonly used in supervised learning models.
Reason (R): Supervised learning depends on known outputs to train the model.
Answer: Assertion is false, but Reason is true.
Q8. Assertion (A): Features represent the attributes or properties of data used for model training.
Reason (R): Features help the AI model identify patterns and relationships in the data.
Answer: Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
Q9. Assertion (A): Deep Learning is considered the most advanced form of Artificial Intelligence among AI, ML and DL.
Reason (R): Deep Learning systems can automatically learn representations from raw data using multiple ML algorithms.
Answer: Both Assertion and Reason are true, and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
Q10. Assertion (A): Testing data is used to evaluate the performance of a trained AI model.
Reason (R): Testing data is always labeled and used to train the model.
Answer: Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
Section B: Fill in the Blanks (10)
Q1. AI Modelling involves developing __________ to get intelligent outputs.
Answer: algorithms
Q2. Rule-based AI follows rules defined by the __________.
Answer: developer
Q3. Rule-based systems usually use __________ statements.
Answer: IF–THEN
Q4. Learning-based models learn from __________.
Answer: data
Q5. Spam email filtering uses a __________ based approach.
Answer: learning
Q6. Supervised learning requires __________ data.
Answer: labeled
Q7. Classification models work on __________ data.
Answer: discrete
Q8. Regression models predict __________ values.
Answer: continuous
Q9. Predicting temperature is an example of __________.
Answer: regression
Q10. Machine Learning and Deep Learning come under __________ based approach.
Answer: learning
Section C: Short Answer Questions
(Answer in about 30 words)
Q1. What is AI Modelling?
Answer: AI Modelling is the process of creating algorithms or models that enable machines to learn from data and produce intelligent outputs or predictions.
Q2. What is a rule-based approach in AI?
Answer: A rule-based approach is an AI model where predefined rules created by the developer guide the machine’s decisions using IF–THEN logic.
Q3. State one advantage of rule-based AI.
Answer: Rule-based AI is easy to understand and implement since decisions are based on clearly defined rules.
Q4. State one limitation of rule-based AI.
Answer: Rule-based AI is static and cannot adapt or learn from new data or feedback.
Q5. What is a learning-based approach?
Answer: A learning-based approach allows machines to learn patterns from data and improve performance without explicit rule programming.
Q6. Why is learning-based AI more flexible?
Answer: Learning-based AI adapts to changes in data and improves accuracy over time by learning from experience.
Q7. What is supervised learning?
Answer: Supervised learning is a type of machine learning where the model is trained using labeled data with known outputs.
Q8. What is classification in supervised learning?
Answer: Classification assigns input data to predefined categories such as spam or not spam.
Q9. What is regression in supervised learning?
Answer: Regression predicts continuous values such as temperature, price or income based on input data.
Q10. Give one real-life example of regression.
Answer: Predicting house prices based on size, location and number of rooms is a regression example.
Section D: Long Answer Questions
(Answer in at least 80 words)
Q1. Explain Rule-Based AI Modelling with an example. Mention one drawback.
Answer: Rule-based AI modelling uses predefined rules created by the developer to make decisions. These rules are often written as IF–THEN statements. For example, a rule-based chatbot answers customer queries by matching keywords with predefined responses. If the user’s query matches a rule, the chatbot provides the stored response. The main drawback of this approach is that it is static. The system cannot learn from new data or adapt to situations that were not covered during rule creation.
Q2. Explain Learning-Based AI Modelling with reference to a spam email filter.
Answer: Learning-based AI modelling allows machines to learn from data and improve automatically. In a spam email filter, the model is trained using labeled emails marked as spam or not spam. It learns patterns such as specific words, sender details and attachments. Once trained, it can classify new emails accurately. Over time, the filter improves as it encounters more examples. This adaptability makes learning-based models more effective than rule-based systems.
Q3. Differentiate between Rule-Based and Learning-Based AI Models.
Answer: Rule-based AI models follow fixed rules defined by the developer and do not learn from new data. They are simple but rigid. Learning-based AI models learn patterns from data and improve over time. Rule-based systems are static, while learning-based systems are adaptive. Rule-based AI works well for simple tasks like FAQs, whereas learning-based AI is used in spam detection, recommendations and image recognition.
Q4. Explain Supervised Learning with examples of classification and regression.
Answer: Supervised learning uses labeled data to train models. In classification, data is grouped into categories such as spam or not spam, hot or cold weather. The output is discrete. In regression, the model predicts continuous values such as temperature or house price. For example, predicting whether a student passes or fails is classification, while predicting a student’s marks is regression.
Q5. Why is regression used for price prediction problems? Explain with an example.
Answer: Regression is used for price prediction because prices are continuous values. In house price prediction, the model uses features like number of bedrooms, carpet area and garage size to predict the price. Since price can vary across a wide range and is not fixed to categories, regression models are best suited for such problems.
Section E: Competency-Based / Case-Study Questions
Q1. A school has introduced an AI-based chatbot on its website to answer students’ queries related to admission process, fee structure, school timings and holidays. The chatbot replies only from a fixed set of responses already stored in the system. If a student asks a question that is not present in the database, the chatbot fails to give a proper response.
Identify the type of AI model used in this system. Explain how this model works and mention one limitation based on the given situation.
Answer:
The chatbot is using a rule-based AI model. In this approach, the system works on predefined rules written by the developer, usually in the form of IF–THEN statements. When a user asks a question, the chatbot matches it with stored rules and provides the corresponding response. Since the chatbot cannot learn from new queries or update itself automatically, it fails when an unfamiliar question is asked. The major limitation of this model is that it is static and cannot adapt or improve with experience.
Q2. An email service provider uses an AI system to automatically detect spam emails. The system improves its accuracy over time as users mark emails as “spam” or “not spam”. Based on this feedback, the AI model updates itself and makes better predictions for future emails.Identify the AI approach used in this system. Explain how learning takes place and why this approach is suitable for the given problem.
Answer:
The system uses a learning-based AI approach. In this model, the AI learns patterns from data instead of following fixed rules. When users label emails as spam or not spam, the system uses this labeled data to improve its prediction accuracy. Over time, it learns new patterns such as suspicious keywords, sender behavior and attachments. This approach is suitable because spam patterns keep changing, and a learning-based model can adapt to new types of spam, unlike rule-based systems.
Q3. A weather forecasting system predicts the temperature of a city for the next day using past data such as humidity, wind speed and atmospheric pressure. The output of the system is a numeric value like 32.5°C or 18.7°C.
Identify the type of supervised learning used here. Justify your answer and explain why classification is not suitable in this case.
Answer:
The system uses regression, which is a type of supervised learning. Regression is used when the output is a continuous numeric value, such as temperature. In this case, the predicted temperature can take any value within a range, making regression the correct choice. Classification is not suitable because it assigns data into fixed categories, such as hot or cold. Since exact temperature values are required for accurate weather forecasting, regression models are more appropriate.
Q4. An online shopping platform uses AI to predict whether a customer will buy a product or not based on their browsing history, time spent on product pages and past purchase records. The system gives outputs like “Yes” or “No”.
Identify the type of AI model and learning technique used. Explain your reasoning with reference to the output type.
Answer:
The system uses a learning-based AI model with supervised learning, specifically classification. The model is trained on labeled data where previous customer behavior is linked with outcomes such as purchase or no purchase. Since the output is categorical and limited to fixed classes like “Yes” or “No”, classification is the correct technique. Learning-based models are suitable because customer behavior patterns change over time and the system can improve accuracy as more data becomes available.
Q5. A company initially used a rule-based AI system to recommend products to customers. However, the recommendations did not improve even after thousands of users interacted with the platform. Later, the company replaced it with a learning-based model, and the quality of recommendations improved significantly.
Explain why the learning-based model performed better than the rule-based model in this scenario.
Answer:
The learning-based model performed better because it could learn from user interaction data and adapt over time. Unlike rule-based systems, which follow fixed rules and cannot change unless manually updated, learning-based models analyze patterns such as user preferences, browsing history and purchases. As more users interacted with the system, the model refined its recommendations automatically. This adaptability and continuous improvement make learning-based AI more effective for dynamic and data-driven applications like product recommendation.
By Anjeev Kr Singh – Computer Science Educator
Published on : January 17, 2026 | Updated on : January 17, 2026