Class 10 AI Code 417 Unit 2: Advanced Concepts of Modelling in AI – Unsupervised & Reinforcement Learning Notes with Worksheet
Unsupervised Learning
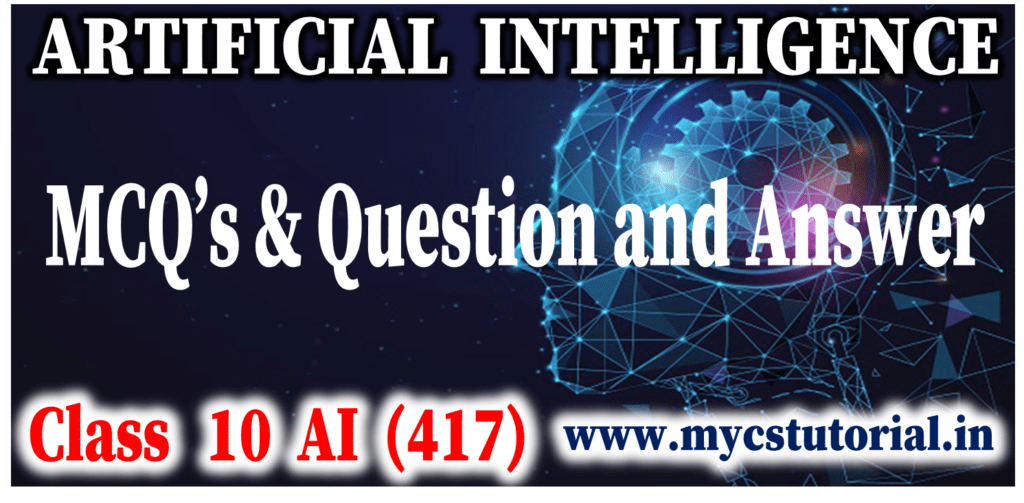
An unsupervised learning model works on an unlabelled dataset. Unsupervised Learning is a type of learning without any guidance.
- This means that the data which is fed to the machine is random and there is a possibility that the person who is training the model does not have any information regarding it.
- The unsupervised learning models are used to identify relationships, patterns and trends out of the data which is fed into it. Here, the machine is responsible to discover patterns, similarities, and differences on its own based on the unlabeled dataset.
- It helps the user in understanding what the data is about and what are the major features identified by the machine in it.
Unsupervised Learning – Example
- Example – 1: Identifying Dogs
- You have a random dataset of 1000 dog images, and you wish to understand some pattern out of it, you would feed this data into the unsupervised learning model and would train the machine on it.
- After training, the machine would come up with patterns which it was able to identify out of it.
- The Machine might come up with patterns which are already known to the user like colour or it might even come up with something very unusual like the size of the dogs.
- Example – 2: Learning of swimming technique by a child
- A child learning to swim on his own without any supervision.
- Here, the child is the model trying to discover ways and techniques to swim and the swimming pool is similar to the unknown data fed to the model.

- Example – 3: Sending a Grocery Offer to Supermarket customer
- Assume that we have a customer database with records of their products bought over a period.
- Now you, being the marketing manager, decide to send a grocery offer message to those customers who buy groceries regularly.
- Note that there were no customers labeled as grocery shoppers and non-grocery shoppers.
- The model could discover patterns on its own and could come up with these two clusters/groups.
- Example – 4:Classifying the shapes
- In the example shown in the image, the model has to process information without any labels.
- It has to analyze and process the data to identify hidden patterns and attributes and then uses that to classify the shapes into three categories based on similarities.
- As you observe in the image, input is not labelled but the model can come up with three clusters by identifying similar patterns and attributes and has grouped them together-
- All squares have been grouped into cluster 1.
- All circles have been grouped into cluster 2.
- All triangles have been grouped into cluster 3.
Sub-categories of Unsupervised Learning Model
Unsupervised learning models can be further divided into two categories:
(a) Clustering model and (b) Association model.
a) Clustering Model:
Clustering is a process of dividing the data points into different groups or clusters based on their similarity between them.
- In this example, we have input data with no class labels (unlabeled data), and this input data comprises birds and animals.
- Note that, even though there were no class labels, the unsupervised learning model was able to divide this data into two clusters based on clustering.
- The two clusters have been formed based on the similarity of characteristics.
- The first cluster comprises all the animals, and the second cluster comprises all the birds.
Difference between Clustering vs Classification
| Classification (Supervised Learning) | Clustering (Unsupervised Learning) |
| Classification uses predefined classes in which objects are assigned. | Clustering finds similarities between objects and places them in the same cluster, and it differentiates them from objects in other clusters. |
Examples of Clustering Model:
Jim enjoys listening to music. Jim likes to listen to music having slow tempo and soft intensity whereas he dislikes songs having fast tempo and high intensity.
- We have grouped all the songs having slow tempo and soft intensity into 1 cluster that he likes
- While, songs with a fast tempo and high intensity into another cluster.
- Now if he listens to a new song X with a slow tempo and soft intensity. Could you predict whether he will like the song X or not?
- This is how clustering techniques work. The clustering model will be able to identify clusters based on some similarities or patterns which are not defined in the input.
- For example, tempo and intensity are the only features known, but clusters based on likes and dislikes have been grouped together and given as output.
- Similar techniques are used in OTT platforms like Netflix/Spotify for recommendations.
b) Association Model:
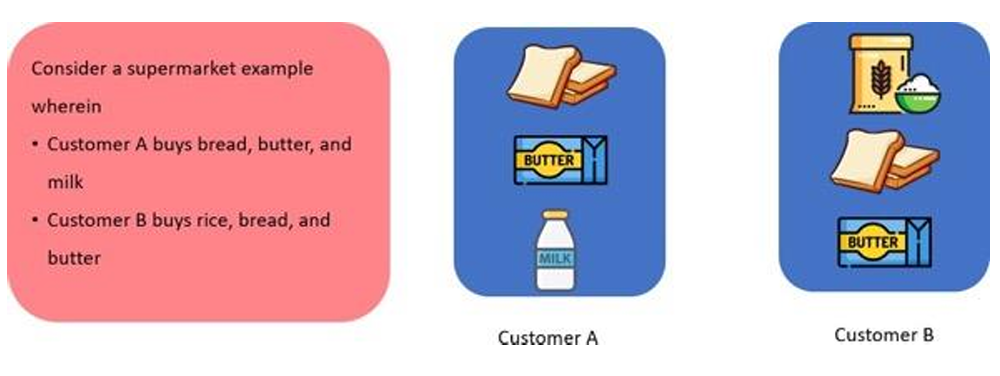
- Association Rule is an unsupervised learning method that is used to find interesting relationships between variables from the database.
- Example:

- Based on the purchase pattern of customers A and B, can you predict any Customer X who buys bread will most probably buy?

- Based on the purchase pattern of other customers, we can predict that there is a high probability that any customer x who buys bread will most probably buy butter.
- Therefore, such meaningful associations can be useful to recommend items to customers. This is called Association Rule.
Test Your Learning
Identify the model: Supervised or Unsupervised ?
- Case 1: Social Media platforms identify your friend in a picture from an album of tagged photographs.
- It is supervised learning. Here social media platform is using tagged photos to recognize the person. Therefore, the tagged photos become the labels of the pictures and we know that when the machine is learning from labeled data, it is supervised learning.
- Case 2: OTT platform Recommendations based on someone’s watch history.
- It is unsupervised learning. This is what OTT platforms like Netflix, Pandora, and Spotify do all the time; they collect the songs/movies that you like already, evaluate the features based on your likes/dislikes and then recommend new movies/songs based on similar features.
- Case 3: Analyse bank data for suspicious-looking transactions and flag the fraud transactions [Note that suspicious transactions are not defined in this case]
- It is unsupervised learning. In this case, the suspicious transactions are not defined, hence there are no labels of “fraud” and “not fraud”. The model tries to identify outliers by looking at anomalous transactions and flags them as ‘fraud’.
Difference between Supervised Learning and Unsupervised Learning
| Supervised Learning | Unsupervised Learning |
| Deals with labelled data. Useful in real-world problems – like, predicting the price of an item based on past trends. Computing power required is simpler as clean labelled data is used as input. | Deals with unlabelled data.Useful in finding unknown patterns within data – like making sense of a large number of observations from an experimental device.The computing power required is more complex as unsorted and messy data is used as input. |
Reinforcement Learning
- This learning approach enables the computer to make a series of decisions that maximize a reward metric for the task without human intervention and without being explicitly programmed to achieve the task.
- Reinforcement learning is a type of learning in which a machine learns to perform a task through a repeated trial-and-error method.
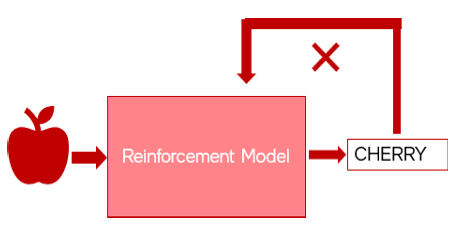
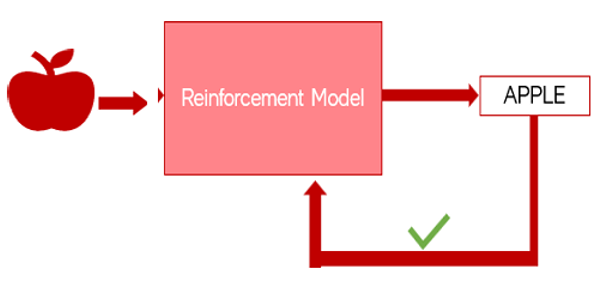
Reinforcement Learning – Example
- Let’s say you provide an image of an apple to the machine and ask the machine to predict it.
- The machine first predicts it as ‘cherry’ and you give negative feedback that it’s incorrect.
- Now, the machine learns that it’s not a cherry
- Then again, you ask the machine to predict the fruit by giving an image of an apple as input;
- Now, it knows it is not a cherry. It predicts it as an apple and you give positive feedback that it’s correct.
- So, now the machine learns that this is an apple.
How is Reinforcement Learning different from supervised and Unsupervised Learning?
- For supervised learning and unsupervised learning, you need to have a pretty good idea of the data that you have, what’s going on, and how to solve the problem.
- However, you will frequently encounter situations where you have to deal with large complex problem spaces.
- You may need to respond to unforeseen environments, and you don’t have sufficient data on those specific scenarios.
- The environment may change. Hence your system needs to be adaptive. Reinforcement Learning will be important because it doesn’t require a lot of pre- existing knowledge or data to provide useful solutions.
Examples of Reinforcement Learning
Humanoid walking

Parking a Car

Video Link:
- Parking a Car: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VMp6pq6_QjI&t=28s
- Humanoid Walking: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gn4nRCC9TwQ
Summary of ML Models
- Supervised learning models are used when we want to determine relationships through training.
- Unsupervised learning models are used when we want to discover new patterns from data.
- Reinforcement learning models are used when we want to implement machine learning through a reward mechanism.
| Topics | Video Link | Notes, Worksheet & QnA |
|---|---|---|
| 2.1 Revisiting AI, ML, DL | Watch Video | Notes, Worksheet & QnA |
| 2.2 (a) AI Modelling – Rule-Based, Learning Based, Machine Learning, Supervised Learning | Watch Video | Notes, Worksheet & QnA |
| 2.2 (b) AI Modelling – Unsupervised & Reinforcement Learning | Watch Video | Notes, Worksheet & QnA |
Class 10 – Artificial Intelligence Code 417 Unit-2: Advanced Concepts of Modelling in AI
Worksheet
Section A: Multiple Choice Questions
- An unsupervised learning model works on
A) Labeled data
B) Unlabeled data
C) Partially labeled data
D) Test data
Answer: B - Which learning approach discovers hidden patterns without guidance?
A) Supervised
B) Reinforcement
C) Unsupervised
D) Rule-based
Answer: C - Clustering belongs to which category of learning?
A) Supervised learning
B) Reinforcement learning
C) Unsupervised learning
D) Rule-based learning
Answer: C - Which of the following is an example of association rule?
A) Image classification
B) House price prediction
C) Bread → Butter purchase pattern
D) Digit recognition
Answer: C - Identifying animals and birds from unlabeled images is an example of
A) Classification
B) Regression
C) Clustering
D) Reinforcement learning
Answer: C - Which platform mainly uses unsupervised learning for recommendations?
A) Calculator
B) Spreadsheet
C) OTT platforms
D) Word processor
Answer: C - Reinforcement learning is based on
A) Labels
B) Random guessing
C) Reward and penalty
D) Static rules
Answer: C - In reinforcement learning, feedback is given in the form of
A) Labels
B) Rewards
C) Rules
D) Features
Answer: B - Which learning model is suitable for unknown fraud patterns?
A) Supervised
B) Unsupervised
C) Rule-based
D) Manual checking
Answer: B - Grouping songs based on tempo and intensity is an example of
A) Classification
B) Regression
C) Clustering
D) Reinforcement learning
Answer: C - Which learning requires the most computing power?
A) Supervised
B) Rule-based
C) Unsupervised
D) Manual
Answer: C - Learning through trial and error best describes
A) Supervised learning
B) Unsupervised learning
C) Reinforcement learning
D) Classification
Answer: C - Detecting anomalies in bank transactions without labels uses
A) Supervised learning
B) Unsupervised learning
C) Regression
D) Classification
Answer: B - Association rules are mainly used in
A) Weather forecasting
B) Market basket analysis
C) Image recognition
D) Speech recognition
Answer: B - Which learning adapts best to changing environments?
A) Rule-based
B) Supervised
C) Reinforcement
D) Static models
Answer: C
Section B: Assertion–Reason Questions
- Assertion: Unsupervised learning works on unlabeled data.
Reason: The model identifies patterns without prior information.
Answer: Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A. - Assertion: Clustering and classification are the same.
Reason: Both group data based on similarity.
Answer: A is false, R is false. - Assertion: Reinforcement learning does not require predefined datasets.
Reason: The model learns by interacting with the environment.
Answer: Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A. - Assertion: Association rules help in product recommendation.
Reason: They identify relationships between purchased items.
Answer: Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A. - Assertion: Unsupervised learning needs less computing power than supervised learning.
Reason: Unlabeled data is simpler to process.
Answer: A is false, R is false.
Section C: Fill in the Blanks
- Unsupervised learning works on __________ data.
Answer: unlabeled - __________ is the process of grouping similar data points together.
Answer: Clustering - Reinforcement learning uses __________ and __________ as feedback.
Answer: reward, penalty - Market basket analysis uses __________ learning.
Answer: unsupervised - Identifying hidden relationships between items is called __________.
Answer: association - OTT platform recommendations are based on __________ learning.
Answer: unsupervised - Reinforcement learning follows a __________ and error approach.
Answer: trial - Grouping shapes without labels is an example of __________.
Answer: clustering - Detecting fraud without predefined rules uses __________ learning.
Answer: unsupervised - Parking a car autonomously uses __________ learning.
Answer: reinforcement
Section D: Short Answer Questions
- What is unsupervised learning?
Answer: Unsupervised learning is a type of machine learning where the model works on unlabeled data and identifies hidden patterns, similarities, and differences without any external guidance. - Define clustering.
Answer: Clustering is an unsupervised learning technique that groups similar data points into clusters based on shared characteristics without using predefined labels. - What is reinforcement learning?
Answer: Reinforcement learning is a learning approach where a machine learns by trial and error and improves performance using rewards for correct actions and penalties for incorrect actions. - Give one real-life example of unsupervised learning.
Answer: OTT platforms recommending movies or songs based on user watch history is a real-life example of unsupervised learning. - How is feedback given in reinforcement learning?
Answer: Feedback in reinforcement learning is given in the form of rewards for correct actions and penalties or negative feedback for incorrect actions.
Section E: Long Answer Questions
- Explain unsupervised learning with suitable examples.
Answer:
Unsupervised learning is a machine learning approach where the model is trained using unlabeled data. The machine does not know the correct output in advance and discovers patterns on its own. It identifies similarities, differences, and hidden relationships within the data. Examples include clustering customers based on shopping behavior and grouping animals and birds from images without labels. This approach is useful when labeled data is unavailable or expensive to obtain. - Differentiate between supervised and unsupervised learning.
Answer:
Supervised learning works on labeled data where the correct output is known, and the model learns under guidance. It is used for prediction tasks like classification and regression. Unsupervised learning, on the other hand, works on unlabeled data and discovers hidden patterns without guidance. Supervised learning requires less computing power, while unsupervised learning needs more computational resources due to complex pattern discovery. - Describe reinforcement learning and its working mechanism.
Answer:
Reinforcement learning is a learning approach where a machine learns by interacting with an environment. The model takes actions and receives feedback in the form of rewards or penalties. Based on this feedback, it adjusts its future actions to maximize overall rewards. This approach does not require labeled data and is suitable for dynamic environments such as self-driving cars, robotic movement, and game-playing AI systems. - Explain clustering and association models under unsupervised learning.
Answer:
Clustering and association are two important unsupervised learning models. Clustering groups similar data points into clusters based on shared features, such as grouping songs by tempo and intensity. Association models find relationships between variables, such as identifying that customers who buy bread are likely to buy butter. Both models help extract meaningful insights from unlabeled data.
Section F: Competency-Based / Case Study Questions (3)
- A supermarket wants to identify customers who frequently buy groceries without labeling them beforehand. Which learning model should be used and why?
Answer:
Unsupervised learning should be used because customer data is unlabeled. Clustering can identify patterns and group customers based on purchase behavior, helping the supermarket target grocery buyers effectively. - An OTT platform recommends new movies based on a user’s past viewing history. Identify the learning type and justify your answer.
Answer:
This is unsupervised learning because the platform identifies patterns in user preferences without labeled data and recommends similar content based on discovered similarities. - A robot learns to walk by falling multiple times and improving after each attempt. Identify the learning approach used.
Answer:
Reinforcement learning is used because the robot learns through trial and error, receiving feedback in the form of rewards for successful actions and penalties for failures.
By Anjeev Kr Singh – Computer Science Educator
Published on : January 18, 2026 | Updated on : January 18, 2026