Introduction to Database Concepts
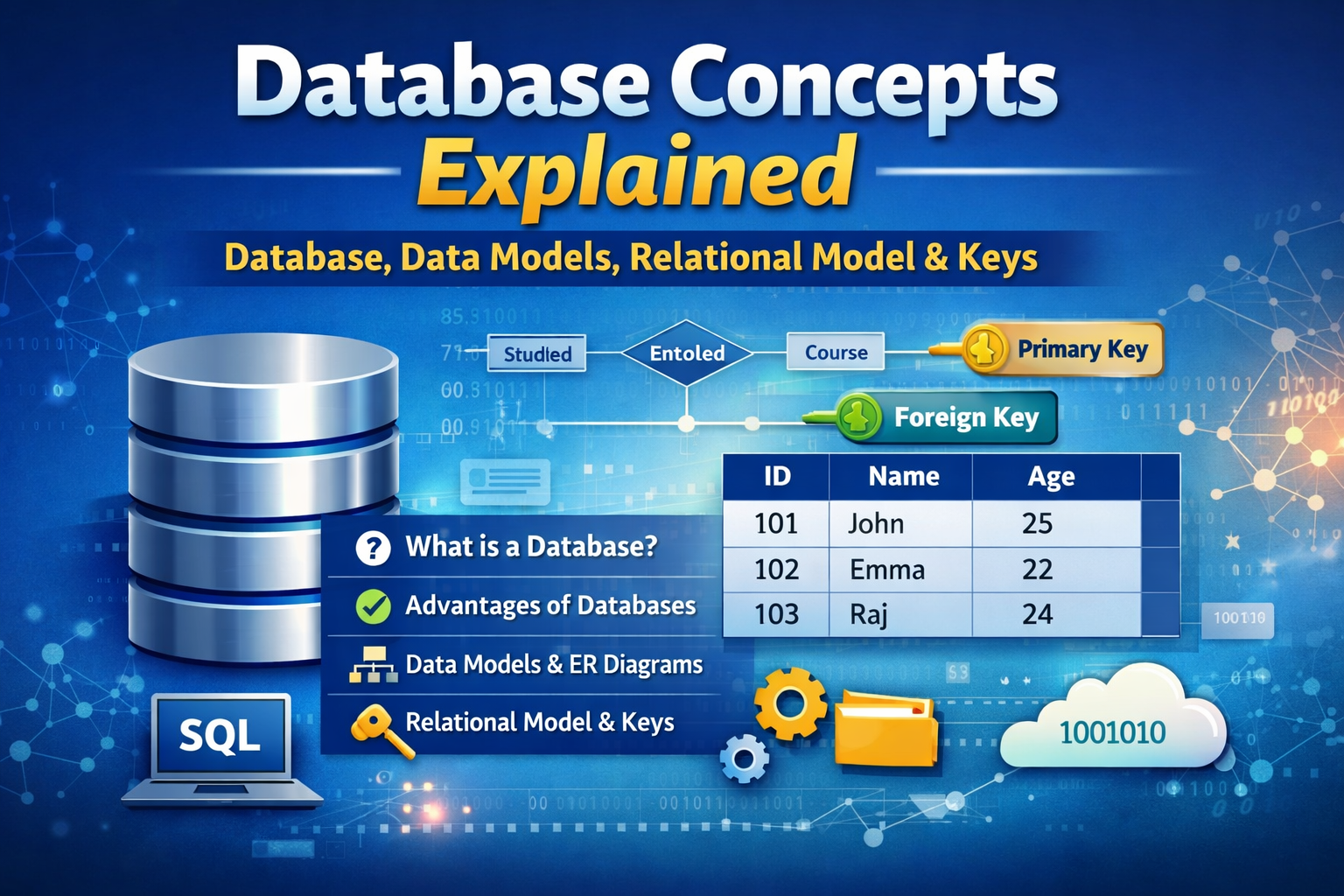
What is a Database?
A database is a systematic collection of organized data or information, typically stored electronically in a computer system. A database allows data to be easily accessed, managed, updated, controlled, and organized.
Frontend & Backend Concept:
Many websites on the World Wide Web use database systems to store and manage data. The database works at the backend, while the user interacts with the frontend.
Advantages of Database
- Minimize Data Redundancy:
In a traditional file processing system, the same data may be stored in multiple files, leading to data redundancy (duplication). A database system minimizes redundancy using data normalization. - Increased Data consistency:
When multiple copies of the same data do not match each other, it leads to data inconsistency. A database helps maintain data consistency. - Data Security:
A database allows only authorized users to access data through authentication and access control mechanisms. - Data Sharing:
Databases allow multiple users to share data simultaneously in a controlled manner. - Data Integrity:
Data integrity ensures that data stored in the database is accurate, consistent, and reliable.
Database Management System (DBMS)
A DBMS is software used to store, manage, and manipulate databases.
Some popular DBMS software includes MySQL, Microsoft Access, Microsoft SQL Server, Oracle Database, FileMaker Pro, and dBASE.
Data Model:
A data model defines how data is organized and represented in a database. Different data models control the structure and relationships of data. The main types of data models are:
- Relational Data Model
- Network Data Model
- Hierarchical Data Model
- Object-Oriented Data Model
Among these, the Relational Data Model is most widely used. In this course, we focus only on the relational data model.
Relational Data Model
In the relational data model:
- Data is organized into tables called relations.
- Tables consist of rows and columns.
- Each row represents a record (tuple).
- Each column represents an attribute (field).
- Tables are related to each other through keys.
Relational Database:
A relational database is a collection of related tables. It allows users to store data in a structured format and establish relationships among tables.
It uses Structured Query Language (SQL) to retrieve, insert, update, and delete data efficiently.
Relational Database Terminologies

- Tuple / Record: A row in a table is called a tuple or record.
- Attribute / Field: A column in a table is called an attribute or field.
- Cardinality: Total number of records (tuples) in a table.
- Degree: Total number of attributes (columns) in a table.
- Domain: The permitted range of values for an attribute.
- Primary Key: An attribute or set of attributes that uniquely identifies a record in a table.
Types of Keys:
- Candidate Key: A Candidate key is an attribute/set of attributes that uniquely identifies tuples in a relation. A relation may have more than one candidate key.
- Primary Key: A Primary key is an attribute/set of attributes that uniquely identifies tuples in a relation. All the values in the primary Key need to be unique and NOT NULL.
- Among all the candidate keys, the Database Administrator(DBA) selects one as the Primary key. A relation may have multiple Candidate Keys, but ONLY ONE Primary Key.
- Composite Key: When two or more than two keys works as a primary key, is called Composite keys.
- Alternate Key: An alternate key is basically is/are a candidate key that is/are not used as the Primary key of the relation.
- Foreign Key: A Foreign key is an attribute of a relation(called as Child table) that refers to the Primary Key of another relation(called as parent table).
Conclusion
A database is an organized collection of data that allows easy storage, retrieval, and management of information. Unlike the traditional file system, which suffers from data redundancy, inconsistency, poor security, and limited data sharing, a database system provides an efficient and reliable way to manage large amounts of data.
A Database Management System (DBMS) is software used to create, store, and manage databases. It ensures data security, integrity, consistency, and controlled access to data. Popular DBMS software includes MySQL, Oracle, and Microsoft SQL Server.
Data in a database is organized using a data model. Among various data models, the Relational Data Model is the most widely used. In this model, data is stored in tables called relations, consisting of rows (tuples) and columns (attributes).
A relational database uses SQL (Structured Query Language) to efficiently retrieve and manipulate data. Relationships between tables are established using different types of keys such as Primary Key, Candidate Key, Composite Key, Alternate Key, and Foreign Key. These keys help maintain data integrity and ensure proper linkage between tables.
Overall, database concepts form the foundation of modern information systems and are essential for effective data management in real-world applications.
Class 12 Computer Science Code 083(PYQB & SQP)
📌 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) – Database Concepts
🔹 A. Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
1. What is a database?
A. A programming language
B. A collection of unorganized files
C. A systematic collection of organized data
D. A computer virus
✅ Answer: C
2. Which software is used to manage databases?
A. Compiler
B. Operating System
C. DBMS
D. Browser
✅ Answer: C
3. Which data model is most widely used in DBMS?
A. Hierarchical
B. Network
C. Object-Oriented
D. Relational
✅ Answer: D
4. Rows in a relational table are called:
A. Attributes
B. Domains
C. Tuples
D. Fields
✅ Answer: C
5. Which key uniquely identifies a record in a table?
A. Foreign Key
B. Composite Key
C. Primary Key
D. Alternate Key
✅ Answer: C
6. The total number of rows in a table is known as:
A. Degree
B. Domain
C. Cardinality
D. Attribute
✅ Answer: C
🔹 B. Assertion–Reason Questions
Options:
A. Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
B. Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A
C. A is true, R is false
D. A is false, R is true
- Assertion (A): A primary key cannot contain NULL values.
Reason (R): A primary key uniquely identifies each record in a table.
✅ Answer: A
2. Assertion (A): Data redundancy is reduced in a database system.
Reason (R): Databases use normalization techniques.
✅ Answer: A
3. Assertion (A): A relation can have more than one primary key.
Reason (R): A relation may have multiple candidate keys.
✅ Answer: D
(Only one primary key is allowed)
🔹 C. True or False
| Statement | True / False |
|---|---|
| A database allows only authorized users to access data. | True |
| A table can have multiple primary keys. | False |
| SQL is used to communicate with a relational database. | True |
| Cardinality refers to number of columns in a table. | False |
| Foreign key is used to link two tables. | True |
| A tuple represents a row in a table. | True |
🔹 D. Short Answer Questions (2–3 Marks)
1. What is DBMS?
A DBMS is software used to create, store, manage, and manipulate databases efficiently.
2. Define data redundancy.
Data redundancy refers to the duplication of data at multiple places in a file system or database.
3. What is a data model?
A data model defines how data is structured, stored, and related in a database.
4. What is a relational database?
A relational database stores data in tables (relations) consisting of rows and columns, and uses keys to establish relationships.
5. Define primary key.
A primary key is an attribute or set of attributes that uniquely identifies each record in a table and cannot contain NULL values.
6. What is a foreign key?
A foreign key is an attribute in a child table that refers to the primary key of a parent table.
7. What is cardinality in a table?
Cardinality is the total number of records (rows) in a table.
8. What is degree in a relation?
Degree refers to the total number of attributes (columns) in a table.
9. What is the difference between a file system and DBMS?
A file system stores data in separate files, whereas a DBMS manages data efficiently with reduced redundancy and better security.
10. What is SQL?
SQL (Structured Query Language) is used to retrieve and manipulate data in a relational database.
By Anjeev Kr Singh – Computer Science Educator
Published on : May 5, 2021 | Updated on : December 24, 2025


