NCERT Book Exercise Solution
Question and Answer
Ch. 10 – Computer Network
10. What do you mean by a modem? Why is it used?
Answer: Modem stands for ‘MOdulator DEModulator’. It refers to a device used for conversion between analog signals and digital signal.
Modem converts digital signals to analog signal (audio frequency) tones which are in the frequency range that the telephone lines can transmit and also it can convert transmitted tones back to digital information.
11. Explain the following devices:
a) Switch
Answer: A switch is a networking device, that plays a central role in a Local Area Network (LAN). Like a hub, a network switch is used to connect multiple computers or communicating devices.
When data arrives, the switch extracts the destination address from the data packet and looks it up in a table to see where to send the packet. Thus, it sends signals to only selected devices instead of sending to all. It can forward multiple packets at the same time. A switch does not forward the signals which are noisy or corrupted. It drops such signals and asks the sender to resend it.
b) Repeater
Answer: A repeater is an analog device that works with signals on the cables to which it is connected. The weakened signal appearing on the cable is regenerated and put back on the cable by a repeater.
c) Router
Answer: A router is a network device that can receive the data, analyse it and transmit it to other networks. A router connects a local area network to the internet.
A router can be wired or wireless. A wireless router can provide Wi-Fi access to smartphones and other devices.
d) Gateway
Answer: Gateway serves as the entry and exit point of a network, as all data coming in or going out of a network must first pass through the gateway in order to use routing paths. Besides routing data packets, gateways also maintain information about the host network’s internal connection paths and the identified paths of other remote networks. If a node from one network wants to communicate with a node of a foreign network, it will pass the data packet to the gateway, which then routes it to the destination using the best possible route.
e) NIC
Answer: Ethernet card, also known as Network Interface Card (NIC card in short) is a network adapter used to set up a wired network.
It acts as an interface between the computer and the network. It is a circuit board mounted on the motherboard of a computer
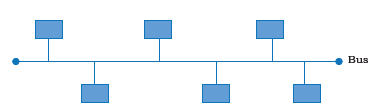
12. Draw a network layout of star topology and bus topology connecting five computers.
Answer: The network topology connecting five computers are:-
Star Topology

Bus Topology
13. What is the significance of the MAC address?
Answer: The address for a device as is identified at the Media Access Control (MAC) layer in the network architecture. MAC address is usually stored in ROM on the network adapter card and is unique.
14. How is an IP address different from MAC address? Discuss briefly.
Answer: IP Address: It refers to a unique numerical label or identifier associated with a computer or a networking device on a network, e.g., 192.168.10.1.
MAC Address: The MAC address refers to the 48-bit physical address assigned to the NIC (Network Interface Controller) of a computer or a networking device on a network, e.g. 00:0A:95:9D:64:18.
15. What is DNS? What is a DNS server?
Answer: DNS stands for Domain Name System. It translates a URL (domain name) into IP address. The Domain Name System works like a telephone directory.
A DNS Server is a computer used to resolve hostnames to IP addresses. For example, a DNS server translates mycstutorial.in to 212.15.25.105 .
16. Sahil, a class X student, has just started understanding the basics of Internet and web technologies. He is a bit confused in between the terms “World Wide Web” and “Internet”. Help him in understanding both the terms with the help of suitable examples of each.
Answer: WWW refers to World Wide Web. It is a set of protocols that allows us to access any document on the Net through URLs. It specifies a way, the HTTP, that allows multimedia and hypertext documents to be opened in web browsers.
The internet is the network of networks that provides the basis of the web. It contains WWW, FTP, Gopher and many more such protocols. WWW is a part of the Internet, which is governed through hypertext, hyperlinks, and HTTP and HTTPS protocols.
Class 12 Computer Science – NCERT Book Exercise Solution
By Anjeev Kr Singh – Computer Science Educator
Published on : January 29, 2022 | Updated on : June 5, 2022