18. What is World Wide Web (WWW)?
Answer: World Wide Web, abbreviated as WWW or W3, is commonly known as the Web.
It is a system of interlinked hypertext documents accessed via the Internet.
19. What is a Web Browser?
Answer: A Web Browser is software used to view Web sites and acts as an interface between the user and the World Wide Web.
20. What are the uses of Web Browser?
Answer: With a web browser, one can view web pages that may contain text, images, videos, and other multimedia, and navigate between them via hyperlinks.
Information is stored on web servers referred to as web pages are retrieved by using a web browser.
21. Give an example of two popular Web Browser software?
Answer: Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Internet Explorer, Firefox, etc.
22. What is a Web Server?
Answer: A web server is a computer that stores websites and their related files for viewing on the Internet.
23. Write five advantages of Networking.
Answer: Advantages of Networking are:-
(a) Data Sharing (b) Hardware Sharing (c) Files Transfer (d) Internet Access Sharing (e) Usage of network-based applications.
24. Expand the following terms: ISP, BSNL, DSL, Wi-Fi, WiMAX, WAP, MODEM, 3G, HSDPA,
Answer: ISP – Internet Service Provider,
BSNL – Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited,
DSL – Digital Subscriber Line,
Wi-Fi – Wireless Fidelity,
WiMAX – Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access,
WAP – Wireless Access Point,
MODEM – MODulator DEModulator,
3G – Third Generation,
HSDPA – High-Speed Downlink Packet Access
25. What is ISP?
Answer: An Internet service provider (ISP) is an organization that provides you with access to the Internet via a dial-up (using a modem) or direct (hard wired) or wireless connection.
26. Give an example of two ISPs?
Answer: Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited (BSNL), Jio, Airtel, MTS, Vodafone, etc.
27. What constraint you must think about before choosing internet connectivity?
Answer: Choosing connectivity depends on the availability of a particular technology, speed, and connection type in your area.
28. What types of connectivity are used by small and medium business or home users?
Answer: Usually small and medium business users, home users use connectivity types such as DSL, cable modem, dial-up, broadband wireless, WiMAX, 3G, 4G, etc.
28. What types of connectivity are used by medium to large business users?
Answer: Medium to large business users or customers with more demanding requirements may use high-speed connectivity such as DSL (High Speed), ISDN, etc.
29. How many types of Internet connectivity?
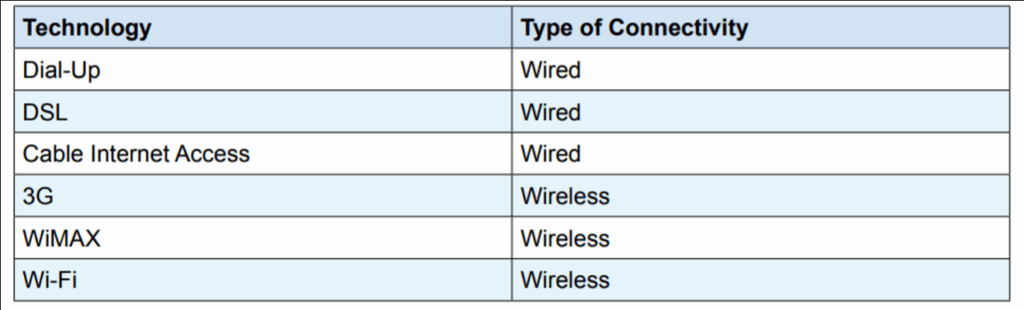
Answer: Broadly Internet connectivity is categorized into two categories – (i) Wired and (ii) Wireless.
Different types of internet connectivity are:-
30. What is Modem?
Answer: Modem stands for MODulator / DEModulator.
Á modem is a device that converts digital computer signals into a form (analog signals) that can travel over phone lines. It also re-converts the analog signals back into digital signals.
31. What do you mean by Dial-up?
Answer: Dial-up Internet access is a form of Internet access that uses the facilities of the public switched telephone network (PSTN) to establish a connection to an Internet service provider.
32. What is ISP?
Answer: ISP provides an internet connection, via telephone lines using a device called MODEM. Users dial a particular number provided by the ISP and gain access to the Internet.
33. What is DSL?
Answer: Digital subscriber line(DSL) provide Internet access by transmitting digital data over wires of a local telephone network.
DSL service is delivered along with wired telephone service on the same telephone line.
On the customer premises, a DSL filter removes the high-frequency interference, enabling simultaneous use of the telephone and data transmission.
34. What is required for a DSL Connection?
Answer: For using a DSL connection, you need
(a) DSL modem and
(b) Subscription.
35. What is Cable Internet Access?
Answer: Cable Internet Access is a form of broadband Internet access that uses the cable television infrastructure.
Cable Internet Access is provided through existing cable TV networks.
This is similar to DSL that is provided over existing telephone lines.
36. What is 3G?
Answer: 3G, short for 3rd Generation is a set of standards used for mobile devices and mobile telecommunication services and networks.
High-Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA) is a 3G mobile telephony communications protocol that allows higher data transfer speeds and capacity.
37. What is WiMAX?
Answer: WiMAX (Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access) is a wireless communications standard designed to provide mobile broadband connectivity across cities and countries through a variety of devices.
WiMAX is a long-range system, covering many kilometers and is typically used where DSL or Cable Internet Access cannot be used.
38. What is Wi-Fi?
Answer: Wi-Fi is a popular technology that allows electronic devices such as computers or mobile phones to exchange data wirelessly over a network, including high-speed Internet connections.
WiFi devices such as personal computers, smartphones, video game consoles, etc. can connect to a network resource such as the Internet through a device called the Wireless Access Point (WAP).
39. How data is transferred on the Internet?
Answer: On the Internet, a large data or web page is broken into several packets. These packets are transferred over the Internet.
(i) Each packet is sent from computer to computer until it finds its destination. Each computer on the way decides where next to send the packet. All packets may not take the same route.
(ii) At the destination, the packets are examined. If any packets are missing or damaged, a message is sent asking for them to be re-sent. This continues until all packets have been received intact.
(iii) The packets are now reassembled into their original form.
Web Application and Security – MCQs and Question Answer
- Class 10 IT 402 Web Application and Security Revision Notes – Download pdf
- Class 10 Info Tech 402 Unit 4 Web Application and Security Notes download pdf
- Class 10 IT Code 402 Unit 4 Web Applications Security Session 11 Protect Health and Safety at Work Question Answer
- Class 10 IT Code 402 Unit 4 Web Applications Security Session 10 Prevent Accidents and Emergencies Question Answer
- Class 10 IT Code 402 Unit 4 Web Applications Security Session 9 Maintain Workplace Safety Question Answer
- Class 10 IT Code 402 Unit 4 Web Applications Security Session 8 Internet Security Question Answer
- Class 10 IT Code 402 Unit 4 Web Applications Security Session 7 Online Transactions Question Answer
- Class 10 IT Code 402 Unit 4 Web Applications Security Session 6 Using Offline Blog Editors Question Answer
- Class 10 IT Code 402 Unit 4 Web Applications Security Session 5 Creating and Publishing Web Pages Blog Question Answer
- Class 10 IT Code 402 Unit 4 Web Applications Security Session 4 Chatting with a Contact Google Talk Question Answer
- Class 10 IT Code 402 Unit 4 Web Applications Security Session 3 Introduction to Instant Messaging 50+ Question Answer
- Class 10 IT Code 402 Unit 4 Web Applications Security Session 2 Networking Fundamentals 50+ Question Answer
- Class 10 IT Code 402 Unit 4 Web Applications Security Session 1 Working with Accessibility Options 50+ Question Answer
Database Management Systems – MCQs and Question Answer
By Anjeev Kr Singh – Computer Science Educator
Published on : February 6, 2022 | Updated on : May 8, 2022
































